Ssd Dram Cache Vs Slc Cache: Which One Is Better?
SSD DRAM cache and SLC cache are two different types of caching technologies used in SSDs to enhance performance.
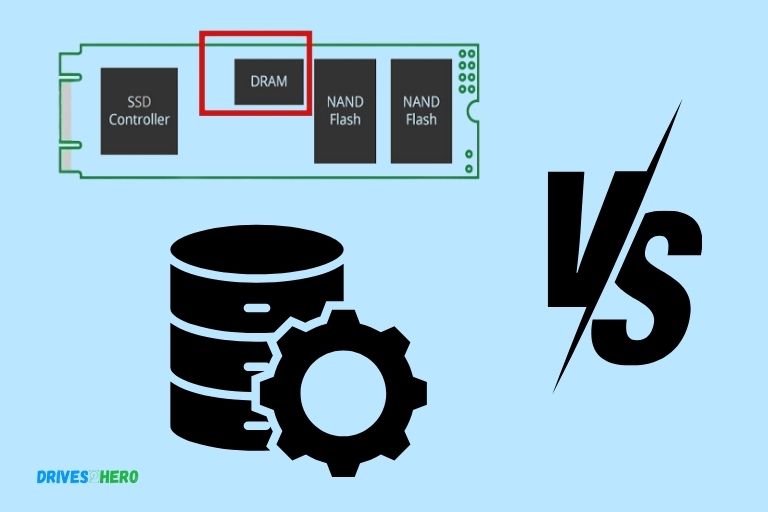
DRAM cache is a separate memory module that stores frequently accessed data for rapid retrieval, while SLC cache uses a portion of the SSD’s NAND storage in a single-level cell (SLC) mode, which allows for faster write speeds.
In terms of performance, both DRAM cache and SLC cache can greatly improve SSD performance. However, they work in different ways.
The DRAM cache is a high-speed volatile memory used to store a map of all data stored on the SSD, allowing for faster data retrieval.
On the other hand, SLC cache works by storing a portion of the SSD’s storage in a high-speed single-level cell mode, which can greatly improve write speeds.
Key Takeaway
Exploring Slc Cache
SSD Dram Cache and SLC Cache are both important components for improving storage performance.
While SSD Dram Cache relies on dynamic random-access memory to enhance speed, SLC Cache utilizes single-level cell technology to provide even faster data access, making it an attractive option for those seeking top-tier performance.
Ssd Dram Cache Vs Slc Cache
SLC Cache, also known as Single-Level Cell Cache, is a caching technology used in solid-state drives (SSDs) to enhance performance and endurance.
It is a type of NAND flash memory that stores one bit of data per cell, making it faster and more reliable than other types of cache.
Definition And Purpose Of Slc Cache
- SLC Cache refers to a small portion of the SSD that is dedicated to storing frequently accessed data.
- Its purpose is to improve the read and write performance of the SSD by accelerating data transfer.
Advantages Of Slc Cache
- Faster Speed: SLC Cache enables quicker data retrieval and writing, leading to improved overall performance.
- Enhanced Endurance: Since SLC Cache stores data in a single bit per cell, it reduces wear on the SSD, increasing its lifespan.
- Improved Reliability: SLC Cache’s single-level cell structure offers better data integrity and reduces the chances of errors or data corruption.
Impact On Performance And Endurance
- Performance: SLC Cache significantly enhances the read and write speeds of an SSD, resulting in faster data access and file transfers.
- Endurance: By utilizing SLC Cache, SSDs can handle heavy workloads without wearing out quickly. With less data movement across the NAND cells, the SSD’s endurance is improved.
Comparison With Ssd Dram Cache
- SLC Cache and SSD DRAM Cache serve similar purposes, improving SSD performance.
- While SLC Cache uses NAND flash memory, SSD DRAM Cache utilizes volatile DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) for caching.
- SLC Cache is more cost-effective than SSD DRAM Cache since NAND flash memory is cheaper to manufacture.
- However, SSD DRAM Cache offers higher speed and durability compared to SLC Cache.
Use Cases And Applications
SLC Cache is beneficial in various scenarios where high-speed data access is crucial:
- Gaming: SLC Cache can accelerate game loading times and improve the overall gaming experience.
- Creative Work: Tasks like video editing or graphic design often require quick file transfers, which SLC Cache can facilitate.
- Database Management: SLC Cache can enhance the efficiency of database operations, ensuring fast data retrieval and processing.
SLC Cache is a valuable caching technology that enhances the performance and endurance of solid-state drives. With its faster speeds, increased endurance, and improved reliability, SLC Cache proves to be a valuable addition to SSDs in a variety of use cases.
Performance Comparison Of Ssd Dram Cache And Slc Cache
The performance of SSD with DRAM cache and SLC cache is compared to determine their effectiveness in storage. By analyzing their capabilities, users can make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
Read And Write Speeds:
SSD DRAM Cache:
- Provides faster read and write speeds compared to SLC cache.
- Dramatically improves the overall SSD performance.
- Delivers faster data access when reading or writing files.
- Reduces latency and enhances the user experience.
SLC Cache:
- Offers competitive read and write speeds but relatively slower than SSD DRAM cache.
- Improves SSD performance by temporarily storing frequently accessed data.
- Enhances responsiveness during regular usage.
- Can maintain solid performance even during high-demand periods.
Endurance And Data Retention:
SSD DRAM Cache:
- Typically has higher endurance due to the use of dynamic random-access memory.
- Provides longer lifespan, making it more suitable for intensive workloads.
- Retains data for a shorter duration after power loss.
- Requires power backup or efficient battery solutions to prevent data loss.
SLC Cache:
- Offers excellent endurance and data retention capabilities.
- Ideal for applications that require high reliability and durability.
- Retains data for a longer duration after power loss.
- Ensures higher level of data protection and integrity.
Effect On Random And Sequential Workloads:
SSD DRAM Cache:
- Performs exceptionally well in both random and sequential workloads.
- Excels in rapidly accessing and transferring data across various file sizes.
- Makes multitasking smooth and efficient.
- Perfect for gamers, content creators, and heavy users.
SLC Cache:
- Demonstrates remarkable performance in random workloads.
- Performs comparatively better with smaller file sizes.
- Still offers respectable performance in sequential workloads.
- Suited for users handling demanding applications and tasks.
Power Consumption And Efficiency:
SSD DRAM Cache:
- Generally consumes more power due to its memory-intensive operations.
- Provides higher speed at the cost of increased power consumption.
- Suitable for desktop PCs or devices with reliable power sources.
- May not be the most energy-efficient choice for laptops or portable devices.
SLC Cache:
- Offers better power efficiency due to simpler data storage structure.
- Consumes less power during read and write operations.
- Ideal for mobile devices and laptops with limited battery capacity.
- Ensures prolonged battery life and enhanced energy efficiency.
Both SSD DRAM cache and SLC cache have their own strengths and weaknesses when it comes to performance. SSD DRAM cache excels in read and write speeds while SLC cache offers excellent endurance and data retention capabilities.
Which Type of Cache is More Effective: SLC or DRAM?
When it comes to enhancing the performance of solid-state drives (SSDs), the “slc cache in SSD: a comprehensive overview” is a crucial aspect to consider. Comparing SLC (single-level cell) to DRAM (dynamic random access memory) cache, their effectiveness depends on the specific requirements. SLC cache, characterized by fast write speeds and high endurance, is more effective for tasks involving frequent write operations and data integrity. On the other hand, DRAM cache offers faster read speeds and is suitable for applications that require rapid access to frequently-accessed data. The choice ultimately depends on the intended use case and the desired balance between write and read performance in an SSD.
Factors To Consider When Choosing A Cache Type
When choosing between SSD DRAM cache and SLC cache, consider factors such as capacity, cost-effectiveness, and performance. SSD DRAM cache offers larger storage capacity, while SLC cache provides faster write speeds.
Use Case And Workload Requirements
- Consider the specific use case and workload requirements of your storage device when choosing a cache type.
- Think about the tasks and activities you will be performing on the device and the workload it will need to handle.
- Analyze whether your use case requires frequent read or write operations or a balanced combination of both.
- Determine the level of data latency tolerance your use case demands, as this will impact cache performance.
- Assess the typical file sizes and types you will be working with to understand the impact on cache utilization.
Budget And Cost Considerations
- Take into account your budget and the cost of the cache type, as different cache technologies have varying price points.
- Evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each cache type in relation to their cost to ensure you get the best value for your money.
- Consider the long-term costs, including maintenance and potential upgrades, associated with the cache type you choose.
Size And Capacity Limitations
- Evaluate the size and capacity limitations of the cache type, especially if you are working with limited storage space.
- Consider the amount of data you need to cache and whether the cache size provided by the cache type is sufficient for your needs.
- Assess the potential impact of cache size on performance and the ability to store frequently accessed data.
Compatibility With Different Storage Devices
- Check the compatibility of the cache type with different storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), hard disk drives (HDDs), or hybrid drives.
- Consider whether the cache type is specifically designed for a particular storage device and if it offers optimal performance in that configuration.
- Determine if the cache type supports common interfaces and protocols, like SATA or NVMe.
Long-Term Reliability And Durability
- Evaluate the long-term reliability and durability of the cache type before making a decision.
- Consider the expected lifespan of the cache type and its ability to withstand heavy usage over time.
- Assess the durability of the cache technology in relation to factors such as power loss protection and wear-leveling algorithms.
To make an informed decision about cache type selection, it’s essential to analyze factors like use case requirements, budget, size limitations, compatibility, and long-term reliability.
By considering these aspects, you can choose the cache type that best suits your specific needs and ensures optimal storage performance.
Conclusion
The discussion of SSD DRAM cache vs SLC cache has shed light on the importance of understanding the differences between these two technologies.
Both options offer benefits and trade-offs. SSDs with DRAM cache excel in terms of speed and performance, making them ideal for high-intensity tasks.
On the other hand, SLC cache provides a more cost-effective solution without compromising too much on performance. Selecting the right option depends on individual needs and budget constraints.
Ultimately, with the proper understanding and careful consideration of your unique circumstances, you can make an informed decision and choose the cache technology that best suits your needs.