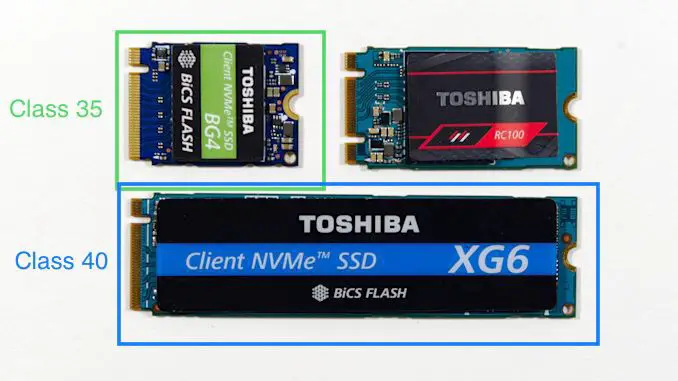
Nvme Ssd Class 35 Vs Class 40: Which One Is Superior?
NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40 are both types of Solid State Drives that offer high-speed performance for storage and application runs.
However, the main difference between them is the speed of data transfer, with Class 40 providing a higher speed than Class 35.
NVMe SSD stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express Solid State Drive. This is a type of storage drive that uses flash memory to store data, providing much faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard drives.
The ‘Class’ denotes levels of performance, with higher numbers indicating faster speeds. Therefore, a Class 40 NVMe SSD is faster than a Class 35.
Both NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40 are efficient and high-speed storage solutions. Class 35 is generally more affordable and offers adequate performance for most users.
However, if your work involves heavy data transfer or high-end gaming, investing in the faster Class 40 NVMe SSD would provide a noticeable increase in performance.
Key Takeaway
10 Features Of Nvme Ssd Class 35 Vs Class 40
| Feature | NVMe SSD Class 35 | NVMe SSD Class 40 |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | PCIe Gen3 x4 | PCIe Gen3 x4 |
| Sequential Read Speed | Up to 3,000 MB/s | Up to 3,400 MB/s |
| Sequential Write Speed | Up to 1,000 MB/s | Up to 3,000 MB/s |
| Random Read (IOPS) | Up to 220K | Up to 410K |
| Random Write (IOPS) | Up to 210K | Up to 405K |
| Endurance (TBW) | Varies by capacity | Varies by capacity |
| Form Factor | M.2 2280 | M.2 2280 |
| NAND Type | Varies (TLC or QLC) | Varies, mostly TLC |
| Typical Power Consumption | Lower than Class 40 | Higher than Class 35 |
| Use Case | Mainstream computing, value-oriented users | High-performance computing, enthusiasts |
Five Facts About NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40
Understanding Nvme Ssd Classifications
Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40 are two different classifications that determine the performance and capabilities of the SSDs. Understanding these classifications is essential for choosing the right SSD for your needs.
When it comes to high-performance storage solutions, NVMe SSDs (Non-Volatile Memory Express Solid State Drives) have revolutionized the market.
These compact yet powerful devices have gained immense popularity due to their lightning-fast read and write speeds. However, not all NVMe SSDs are created equal.
Definition And Purpose Of Nvme Ssd Classification
- NVMe SSD classification is a system used to categorize solid state drives based on their performance capabilities.
- These classifications help consumers and businesses make informed decisions when choosing the most suitable SSD for their specific requirements.
- NVMe SSD classification takes various factors into account, including data transfer rates, endurance, power consumption, and overall performance.
Overview Of Different Nvme Ssd Classes Available In The Market
NVMe SSDs are classified into different classes based on their performance characteristics.
Here’s an overview of the classes commonly available:
- Class 10: Entry-level NVMe SSDs suitable for everyday computing tasks with moderate read and write speeds.
- Class 20: Mid-range NVMe SSDs with improved performance for smoother multitasking and faster data transfers.
- Class 30: High-performance NVMe SSDs designed for power users and professionals who require faster read and write speeds.
- Class 35: Performance-focused NVMe SSDs offering even higher data transfer rates and enhanced endurance compared to Class 30.
- Class 40: NVMe SSDs at the top end of the performance spectrum, delivering blazing fast read and write speeds for demanding applications.
Significance Of Class 35 And Class 40 In Nvme Ssd Hierarchy
Class 35 and Class 40 are two significant NVMe SSD classifications in terms of performance and capability.
Here’s why they are important:
- Class 35 NVMe SSDs offer superior data transfer rates and endurance compared to lower-class SSDs, making them ideal for power users who require high-speed storage solutions.
- Class 40 NVMe SSDs represent the pinnacle of performance in the NVMe SSD hierarchy. With unmatched read and write speeds, these SSDs excel in handling resource-intensive tasks, such as video editing, gaming, and enterprise-level applications.
Understanding the NVMe SSD classifications provides valuable insights into the performance capabilities of these storage devices.
Whether you’re a casual user, professional, or tech enthusiast, knowing the distinctions between classes helps you make educated choices to meet your specific needs.
Performance Comparison Between Nvme Ssd Class 35 And Class 40
The performance of Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40 differs significantly, with Class 40 providing faster speeds and better overall performance compared to Class 35.
The upgrade to Class 40 is recommended for those seeking improved performance and faster data transfer rates. NVMe SSDs have revolutionized data storage, offering lightning-fast speeds and improved performance.
Speed And Throughput Capabilities Of Class 35 Nvme Ssds:
- Class 35 NVMe SSDs are engineered for high-performance computing and demanding workloads.
- These SSDs offer impressive read and write speeds, typically ranging from 3000 MB/s to 5000 MB/s.
- With their excellent throughput capabilities, Class 35 NVMe SSDs ensure smooth multitasking and quicker data access.
Speed And Throughput Capabilities Of Class 40 Nvme Ssds:
- Class 40 NVMe SSDs take performance to the next level, specifically designed for intensive applications and enterprise-level workloads.
- These SSDs provide astonishing read and write speeds, ranging from 5000 MB/s to 7000 MB/s.
- With their remarkable throughput capabilities, Class 40 NVMe SSDs deliver unparalleled speed and performance, perfect for data-intensive tasks.
Real-World Performance Benchmarks And Comparisons:
When considering Nvme SSD options, it’s important to look beyond the theoretical speeds and consider real-world performance benchmarks.
Here is how Class 35 and Class 40 Nvme SSDs compare:
- Class 35 SSDs excel in everyday tasks, such as operating system boot times, application launches, and general file transfers.
- Class 40 SSDs shine when it comes to handling resource-intensive workloads, such as 3D rendering, video editing, and large-scale database operations.
Impact On File Transfer Speeds And Application Performance:
- Class 35 NVMe SSDs offer impressive file transfer speeds, allowing you to move large files quickly and efficiently.
- Applications installed on Class 35 SSDs will experience enhanced load times and improved responsiveness, resulting in a smooth user experience.
- On the other hand, Class 40 NVMe SSDs elevate file transfer speeds to astonishing levels, significantly reducing the time required for data transfers.
- Applications installed on Class 40 SSDs will benefit from lightning-fast load times, ensuring seamless multitasking and enhanced productivity.
When choosing between NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40, consider your specific needs and the level of performance required.
Class 35 provides exceptional speed and capability for most everyday tasks, while Class 40 raises the bar for resource-intensive workloads.
Considerations For Choosing Between Nvme Ssd Class 35 And Class 40
Choosing between Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40 involves considering factors like storage capacity, performance, and price.
Class 40 offers faster speeds and higher durability, making it suitable for intensive workloads, while Class 35 provides a more affordable option for everyday use.
When it comes to choosing between Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40, there are several important factors to consider.
Below are some key points to consider when choosing between Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40:
Intended Usage And Workload Requirements:
Class 35:
- Suitable for general computing needs and everyday tasks
- Ideal for regular office and multimedia use
- Offers reliable performance for common applications and software
Class 40:
- Designed specifically for high-intensity workloads
- Ideal for heavy data processing, video editing, and 3D rendering
- Provides faster data transfer speeds and higher performance for demanding tasks
Cost-Effectiveness And Price-Performance Ratio:
Class 35:
- Generally more affordable compared to Class 40 SSDs
- Offers good performance for its price
- Provides value for money for standard computing needs
Class 40:
- Typically higher in price due to enhanced performance capabilities
- Provides superior performance and speed for intensive workloads
- Offers excellent price-performance ratio for professional users and power users requiring top-notch performance
Durability And Lifespan Considerations:
Class 35:
- Offers sufficient durability and lifespan for everyday computing needs
- Suitable for average usage scenarios
- Provides reasonable longevity for regular users
Class 40:
- Provides enhanced durability and longer lifespan compared to Class 35
- Built to handle heavy workloads and prolonged usage
- Designed for users who require long-term reliability and extended lifespan
Future Scalability And Compatibility Factors:
Class 35:
- Compatible with most systems and devices
- Offers good scalability for future upgrades and expansion
- Suitable for users who prefer flexibility and compatibility
Class 40:
- Designed to meet advanced PCIe Gen 4.0 and future technology standards
- Ensures compatibility with cutting-edge systems and hardware
- Provides future-proofing and scalability for users requiring the latest technologies
Considering these factors is essential when choosing between Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40.
Assess your intended usage, workload requirements, budget, and future compatibility needs to make an informed decision that maximizes performance and suits your specific needs.
Factors Influencing The Performance Of Nvme Ssds
Factors such as the classification of Nvme SSDs (Class 35 Vs Class 40) can significantly impact their performance.
These classifications dictate the speed and efficiency of the SSDs, with Class 40 generally offering faster data transfer rates and improved overall performance.
Let’s explore each of these factors in more detail:
Controller And Firmware Optimizations:
- Intelligent algorithms and optimized firmware play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of NVMe SSDs.
- Dynamic wear leveling algorithms ensure even distribution of data, extending the lifespan of the SSD.
- Advanced error correction mechanisms, such as LDPC (Low-Density Parity Check), help maintain data integrity and reliability.
- Efficient garbage collection algorithms and TRIM support improve overall performance by minimizing write amplification and ensuring quicker access to available storage.
Nand Flash Memory Type And Configuration:
- The type of NAND flash memory used in an NVMe SSD greatly impacts its performance.
- SLC (Single-Level Cell) NAND flash memory provides the highest performance and endurance, making it ideal for demanding applications.
- MLC (Multi-Level Cell) NAND flash memory strikes a balance between performance and cost, suitable for many consumer-grade applications.
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell) NAND flash memory offers higher storage density at a lower cost but sacrifices some performance and endurance compared to SLC and MLC.
- The configuration of NAND flash memory chips, such as parallelism and interleaving techniques, can further enhance performance by enabling faster data transfer rates and improved access times.
Overprovisioning And Caching Techniques:
- Overprovisioning involves allocating a portion of the SSD’s storage capacity for internal use, improving performance and extending the drive’s lifespan.
- SLC caching utilizes a small portion of the SSD’s NAND flash memory to temporarily store frequently accessed or hot data, improving read and write performance for certain workloads.
- DRAM caching uses volatile memory to store frequently accessed data, further enhancing overall performance by reducing latency and improving random access speeds.
Impact Of Power Consumption And Thermal Management:
- Power consumption and thermal management play important roles in SSD performance and longevity.
- Lower power consumption not only helps ensure longer battery life in portable devices but also reduces heat generation and thermal throttling, leading to more consistent performance.
- Effective thermal management techniques, such as heat spreaders and advanced cooling solutions, help dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing performance degradation due to overheating.
By considering these factors, you can choose an NVMe SSD that suits your specific requirements, balancing performance, endurance, and cost to achieve an optimal storage solution for your needs.
Future Trends And Developments In Nvme Ssd Technology
Class 35 and Class 40 Nvme SSDs are leading the future trends in solid-state drive technology.
These advancements promise faster data speeds, increased storage capacities, and improved performance for various applications. Stay ahead of the game with the latest in Nvme SSD technology.
Advances In Nvme Ssd Classifications
- SSDs have experienced significant advancements in recent years, leading to the introduction of new classifications such as Class 35 and Class 40.
- Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40 represent different levels of performance, with Class 40 being more advanced and offering faster speeds and better overall performance.
- These new classifications have emerged to keep up with the rapid pace of technology and to meet the demands of modern applications and workloads.
Emerging Technologies And Their Impact On Performance
- The introduction of emerging technologies has greatly impacted the performance of Nvme SSDs.
- Technologies like 3D NAND flash memory have significantly increased storage capacity, allowing for larger amounts of data to be stored on SSDs.
- The use of PCIe Gen4 and Gen5 interfaces has improved data transfer speeds, resulting in faster file transfers, quicker boot times, and reduced latency.
- The development of new controllers and firmware has also contributed to improved performance, enhancing the overall speed and responsiveness of Nvme SSDs.
Predictions For The Future Of Nvme Ssds
- The future of Nvme SSDs looks promising, with several exciting developments expected in the coming years.
- Continued advancements in NAND flash memory technology will likely lead to even higher storage capacities, allowing users to store more data on their SSDs.
- The adoption of PCIe Gen6 and beyond will further increase the data transfer speeds, enabling faster and more efficient performance.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence are also expected to play a crucial role in optimizing SSD performance, enhancing caching algorithms, and further improving overall reliability.
- As the demand for high-speed storage solutions continues to grow, manufacturers will continue to innovate and introduce new features and technologies to meet the evolving needs of consumers.
The future of Nvme SSDs is promising, with advancements in technology and emerging trends leading to improved performance, faster speeds, and increased storage capacities.
As these developments continue, users can expect even better performance and enhanced overall user experience from Nvme SSDs.
Choosing The Right Nvme Ssd Class For Your Needs
Choosing the right Nvme SSD class, whether it’s class 35 or class 40, is crucial for meeting your specific needs.
The class you select depends on the speed and performance requirements you prioritize. Consider your workload and intended usage to make an informed decision.
Recap Of The Similarities And Differences Between Class 35 And Class 40
- Class 35 and Class 40 refer to the performance categories for NVMe SSDs, with Class 40 being the higher performance option.
- Both Class 35 and Class 40 NVMe SSDs offer significant performance improvements over traditional SATA-based SSDs.
- Both classes utilize the NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) interface, which is specifically designed for solid-state storage technologies.
- Class 35 NVMe SSDs typically offer sequential read speeds of up to 3,000 MB/s, while Class 40 NVMe SSDs can reach speeds of up to 6,500 MB/s.
- When it comes to random read and write speeds, Class 40 NVMe SSDs generally outperform Class 35 SSDs.
- In terms of endurance, Class 40 SSDs usually have a higher Terabytes Written (TBW) rating, indicating their ability to handle more data writes over their lifespan.
Factors To Consider When Making A Decision
When deciding between Class 35 and Class 40 NVMe SSDs, there are several important factors to consider:
- Performance requirements: Evaluate your specific needs and determine if the higher performance of Class 40 SSDs is necessary for your workload. Consider factors such as file transfers, gaming, video editing, or data-intensive applications that require fast read and write speeds.
- Budget: Class 40 NVMe SSDs usually come at a higher price point than Class 35 models. Assess your budget and determine how much you are willing to invest in an SSD.
- Capacity requirements: Consider the amount of storage space you need for your files and applications. Both Class 35 and Class 40 NVMe SSDs offer varying capacities, so choose the one that best suits your requirements.
- Future-proofing: If you anticipate needing higher performance in the future or if you work with data-intensive applications, investing in a Class 40 NVMe SSD may be a more future-proof option.
Recommendations Based On Specific Use Cases And Requirements
Following your specific needs, here are some recommendations for choosing the right NVMe SSD class:
- Gaming enthusiasts: If you are a gamer looking to reduce loading times and improve overall performance, a Class 40 NVMe SSD is highly recommended. The faster read and write speeds will provide a noticeable improvement in game load times and reduce any lag during gameplay.
- Content creators: For professionals working with large media files, such as video editing or 3D rendering, the higher performance of Class 40 NVMe SSDs is essential. The increased sequential and random read/write speeds will greatly enhance workflow efficiency.
- Everyday users: If you primarily use your computer for browsing the internet, word processing, and streaming media, a Class 35 NVMe SSD will provide ample performance for your needs. It offers a significant improvement over traditional hard drives and ensures smooth multitasking.
- Budget-conscious individuals: If you are on a tight budget but still want the advantages of NVMe technology, a Class 35 SSD could be the ideal choice. It offers a good balance between performance and affordability.
Remember, the most important aspect when choosing between Class 35 and Class 40 NVMe SSDs is assessing your individual needs and aligning them with the performance, budget, and capacity considerations.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the right NVMe SSD class for your requirements, ensuring a seamless and efficient computing experience.
FAQ On Nvme Ssd Class 35 Vs Class 40
What is the difference between Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40?
Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40 are both non-volatile memory express (NVMe) solid state drives (SSDs).
The main difference between Class 35 and Class 40 is the amount of storage read/write bandwidths each one offers. Class 35 has up to 3500MB/s read/write bandwidth and class 40 has up to 4000MB/s read/write bandwidth.
How are Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40 used?
Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40 are typically used in computing applications that require high storage speeds and/or high throughput storage applications.
Some of these applications include high-performance gaming and media creation, virtualization, and general purpose computing.
What are the benefits of using Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40?
Nvme Ssd Class 35 and Class 40 offer faster data access and transfer speeds than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
They are also more reliable and durable than HDDs, making them a great option for applications that require high performance and/or higher reliability.
They are often compact in size and require minimal power, making them an ideal choice for applications where space and power are limited.
What are the downsides to using Nvme SSD Class 35 and Class 40?
NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40 may have differences in performance, price, capacity, compatibility, power consumption, and heat generation.
These factors should be considered based on your specific needs and priorities when choosing between them.
Conclusion
The choice between NVMe SSD Class 35 and Class 40 ultimately depends on your specific needs and budget. Both classes offer reliable and fast storage solutions, but Class 40 SSDs are generally capable of delivering higher performance and endurance.
If speed and long-term durability are top priorities for your workload or gaming demands, opting for a Class 40 SSD might be a wise investment.
However, if you are on a tighter budget or have less demanding storage needs, a Class 35 SSD can still provide impressive speed and reliability.
It is crucial to assess your requirements carefully, taking into account factors such as workload intensity, data transfer requirements, and budget constraints.
Remember, the overall functionality and compatibility of your system also play key roles in optimizing the performance of whichever class of NVMe SSD you choose.