Nvme Vs Non Nvme Ssd: Which One Should You Choose?
NVMe SSDs significantly outperform non-NVMe SSDs in terms of speed, efficiency, and overall performance due to their superior architecture and communication protocol.
NVMe, or Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a communication protocol specifically designed for SSDs, which allows them to operate at a much higher speed compared to non-NVMe SSDs.
Non-NVMe SSDs, such as SATA SSDs, utilize older protocols that were originally designed for slower, spinning hard disk drives (HDDs).
As a result, NVMe SSDs can handle more simultaneous input/output operations and have lower latency, translating to dramatic improvements in overall performance.
- Speed: NVMe SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to non-NVMe SSDs.
- Efficiency: NVMe SSDs consume less power, leading to improved battery life and lower energy costs.
- Parallelism: NVMe SSDs support a higher degree of parallelism, which enables them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and more efficiently.
- Compatibility: Non-NVMe SSDs are typically more compatible with older systems, while NVMe SSDs may require specific hardware and software support.
In summary, NVMe SSDs provide a substantial advantage over non-NVMe SSDs when it comes to speed, efficiency, and overall performance.
They are an excellent choice for users who require fast data transfers and minimal latency, such as gamers, content creators, and professionals working with large datasets.
However, it is essential to ensure your system is compatible with NVMe SSDs before upgrading, as they may require specific hardware and software support.
Nvme Vs Non Nvme Ssd
| Feature | NVMe SSD | Non-NVMe SSD (SATA) |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | PCIe | SATA |
| Max Throughput | Up to 32 Gbps (PCIe 3.0 x4) | Up to 6 Gbps (SATA III) |
| Max Sequential Read | Up to 3500 MB/s | Up to 550 MB/s |
| Max Sequential Write | Up to 3300 MB/s | Up to 520 MB/s |
| Latency (I/Os Per Sec) | 10x-20x More IOPS than SATA SSDs | Lower IOPS Than NVMe SSDs |
| Form Factors | M.2, U.2, AIC (Add-In Card) | M.2, 2.5″, mSATA |
| Power Consumption | Generally Lower Power Consumption | Higher Power Consumption |
| Cost | Typically More Expensive | Generally More Affordable |
| Compatibility | Requires PCIe Slot/NVMe Compatible MB | Wide Compatibility with Most Systems |
Key Takeaway
Five Facts About Nvme Vs Non Nvme Ssd
Nvme Vs Non Nvme Ssd: What’S The Difference?
Solid-state drives (ssds) are compact data storage devices that have been developed as an alternative to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Ssds offer several advantages such as faster read and write speeds, lower power consumption, and increased durability.
Ssd technology has evolved over the years, leading to the development of two types of ssds: non-nvme and nvme.
This section will define each type and highlight the differences between them.
Define Nvme Ssd And Non Nvme Ssd
Non-nvme refers to a type of ssd that uses the advanced host controller interface (ahci) protocol to communicate with the computer’s operating system.
Ahci has been the industry standard protocol used by ssds since its inception in 2004.
Meanwhile, the non-volatile memory express (nvme) is a newer protocol specially designed for ssds, which provides direct communication between the ssd and the cpu through the pcie bus interface.
Explain The Technical Differences Between The Two Ssd Types
There are several important technical differences between nvme and non-nvme.
Here are some of the most notable ones:
- Speed: Nvme ssds offer faster read and write speeds than non-nvme ssds. This is mainly because nvme uses a more efficient command queue to communicate with the cpu directly, while non-nvme uses a more complex command queue through the ahci protocol.
- Latency: Nvme ssds also have lower latency than non-nvme ssds. This is due to the more direct communication between the ssd and the CPU.
- Cost: Nvme ssds are generally more expensive than non-nvme ssds due to the newer technology and higher performance offered.
Highlight The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Each Type
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of each type:
Non-Nvme Ssd
Advantages:
- Widely available and compatible with most modern computers
- Lower cost compared to nvme ssds
- Can still deliver fast speeds for most general-purpose applications
Disadvantages:
- Slower speeds and higher latency than nvme ssds
- Limited performance compared to nvme ssds
- Lower endurance and lifespan compared to nvme ssds
Nvme Ssd
Advantages:
- Much faster read and write speeds compared to non-nvme ssds
- Lower latency and improved system responsiveness
- Reliable and durable, with a higher endurance and lifespan compared to non-nvme ssds
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to non-nvme ssds
- Compatibility issues with older computer systems and motherboards that do not support pcie gen 3 or higher.
Nvme ssds provide faster speeds and lower latency than non-nvme ssds. However, they are more expensive and may not be compatible with older computer systems.
Non-nvme ssds remain a viable option for general-purpose use, given a more affordable price point and compatibility with most modern computers.
Performance Comparison Between Nvme And Non Nvme Ssd
Compare The Performance Of Nvme And Non Nvme Ssds
If you’re searching for an ssd for your computer, you’ve probably come across the term “nvme” while researching.
Nvme (non-volatile memory express) is the newest storage technology, and it offers many advantages over traditional storage devices. So, how does nvme compare to non-nvme ssds in terms of performance?
Performance Of Non-Nvme Ssds
Non-nvme ssds use the sata interface and are slower than nvme drives.
While sata ssds offer significant speed advantages over traditional hard drives, they cannot keep up with nvme drives in terms of speed and efficiency.
Here are some key points that affect the performance of non-nvme ssds:
- Sata ssds have lower maximum transfer rates compared to nvme ssds. On average, they offer sequential read/write speeds of up to 550mb/sec and 520mb/sec, respectively.
- The sata interface’s bandwidth limits the speed of non-nvme ssds and can cause performance bottlenecks.
- Non-nvme ssds are getting older and may not be supported by newer motherboards or systems.
Performance Of Nvme Ssds
Nvme drives were created with the intention of pushing the limits of traditional storage devices, and they have been very successful in doing so.
Nvme drives offer faster speeds while reducing latency, making them ideal for power users, gamers, and professionals.
Here are some key points that affect the performance of nvme ssds:
- Nvme drives use a pcie interface, which offers significantly faster speeds than the sata interface. An nvme ssd can achieve sequential read/write speeds of 3,500mb/sec and 3,000mb/sec or even higher, depending on the drive.
- Nvme ssds have a lower latency rate than sata ssds, resulting in much lower application loading times. This is because they bypass the operating system’s storage stack and interface directly with the CPU.
- They are powered by faster nvme controllers that enable them to manage more queue lines, increasing their efficiency.
In a nutshell, nvme drives are significantly faster than sata ssds and can reduce latency, making them the ideal choice for power users, gamers, and professionals.
However, non-nvme ssds are still suitable for standard users looking for faster speeds than traditional mechanical drives.
It’s worth noting that external factors like the age of your system, the number of cores on your cpu, and the quality of your motherboard can also affect the performance of both nvme and non-nvme ssds.
Nonetheless, you can always upgrade to a nvme drive and enjoy the benefits of this superior storage technology.
Which Ssd Type Is Best For Your Computer?
Ssds have replaced traditional hard drives due to their lightning-fast speed, durability, and power efficiency features.
However, with emerging ssd technology, choosing the right ssd type for your computer can be overwhelming. Two popular types of ssds are nvme (non-volatile memory express) and non-nvme.
In this blog, we will discuss the factors to consider when choosing an ssd and explain which type of ssd is best for specific use cases, such as gaming and video editing.
We will also provide recommendations for the best nvme and non-nvme ssds on the market.
Discuss The Factors To Consider When Choosing An Ssd
When choosing an ssd, there are several factors to consider as they can impact the ssd’s performance, speed and effectiveness.
These factors are:
- Capacity: Ssds are available in varying capacities, usually ranging from 128gb up to 2tb or more. Choose an ssd that suits your storage needs.
- Interface: The type of interface determines how the hard drive communicates with the computer. Nvme ssds use the pcie interface, allowing for a higher number of input/output operations per second (iops), whereas non-nvme ssds use sata interfaces.
- Speed: The speed at which ssds read and write data determines the ssd’s performance. Nvme ssds have higher transfer rates compared to non-nvme ssds.
- Durability: Ssds boast greater durability due to their lack of moving parts compared to traditional hard drives. Nvme ssds are considered more durable than non-nvme ssds because they use a more advanced type of memory, thereby reducing the risk of data loss.
Explain Which Type Of Ssd Is Best For Specific Use Cases, Such As Gaming, Video Editing, Etc.
The following types of ssds are best suited for specific use cases according to their corresponding requirements:
- Gaming: Gaming requires high-speed read and write operations. Nvme ssds are best for gaming because of their ability to load games more quickly.
- Video editing: Video editing requires a large amount of storage and a high-speed drive. Nvme ssds xpg sx8200 and samsung 970 pro are the best choices for video editing.
- General productivity: An ssd with high durability and speed is best suited for general productivity. Ssds such as sandisk ssd plus and crucial mx500 are great choices for general productivity.
Include Recommendations For The Best Nvme And Non-Nvme Ssds On The Market
The following are some of the best nvme and non-nvme ssds to empower your computer:
- Best nvme ssds: Samsung 970 evo plus, crucial p5, and sabrent rocket q.
- Best non-nvme ssds: Samsung 860 evo, crucial mx500, sandisk ssd plus.
Choosing an ssd for your computer is a crucial decision. Consider various factors to determine the best ssd for your computer to meet its operational needs.
Nvme and non-nvme ssds both offer excellent performance, durability, and speed, so choosing the right one requires a careful balance of budget, capacity, and performance priorities.
Whichever ssd you choose, an ssd upgrade is guaranteed to boost your computer’s performance.
How To Install Your Ssd
Solid-state drives (ssds) are becoming more popular day by day due to their high speed and low power consumption.
A new challenge arises when it comes to choosing an ssd for your computer: whether to go for an nvme or non-nvme ssd.
After making a decision, the next step is to install it. Let’s take a look at how to install an ssd, the best practices to follow, and the common issues users may encounter during installation.
Provide A Step-By-Step Guide To Installing An Ssd
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to install your ssd:
- First, power off your computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open up your computer’s case and locate the hard drive bay or the m.2 slot for slot-in type ssds.
- Remove any cables connected to the hard drive or remove any screws securing the m.2 ssd.
- Carefully slide out the old hard drive or insert the m.2 ssd into the connector slot.
- Screw it into place if necessary.
- Connect the necessary cables if it is a traditional ssd, and securely fasten them.
- Put the computer case back together and reconnect it to the power supply.
Include Tips And Best Practices
Here are some tips and best practices to follow while installing an ssd:
- Always unplug your computer from the power source before attempting to install anything.
- Read your computer’s manual before installing your ssd to avoid any compatibility issues.
- Handle ssds with care. Do not touch the connectors with your fingers, and try to avoid static electricity.
- Keep your ssd firmware up-to-date to improve efficiency and avoid possible issues.
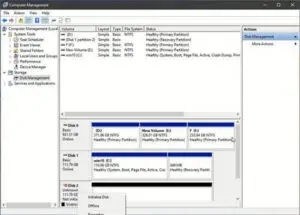
- Remember to initialize the ssd and partition it for using after installation.
Mention Any Common Issues Users May Encounter During Installation
Users may experience some problems during ssd installation if they are not careful.
Here are some common issues:
- Compatibility problems with the motherboard or operating system.
- Poorly seated connections or loosely applied screws leading to connection issues.
- Bios settings not adjusted to recognize the ssd.
- Worn-out sata/power cables leading to data transfer errors.
By following the steps mentioned above and keeping these tips and issues in mind, you can install your ssd with ease and avoid any compatibility issues or installation errors.
Frequently Asked Questions On Nvme Vs Non Nvme Ssd
What Is An Nvme Ssd?
Nvme stands for non-volatile memory express, which is an ssd designed for faster data transfer.
What’S The Difference Between Nvme And Non-Nvme Ssds?
Nvme ssds are significantly faster than their sata counterparts because of their better bus interface and protocol.
What Are The Benefits Of Nvme Ssds?
Nvme ssds are ideal if you want to speed up your system’s boot time and improve application load times.
Are Nvme Ssds Worth The Investment?
For gamers, video editors, and other demanding professionals, an nvme ssd is a beneficial investment. However, for regular users, the difference in performance may not be noticeable.
Conclusion
After weighing all the factors, it’s clear that the decision to choose between nvme and non-nvme ssds depends on the specific needs of your system.
If you’re an average user looking for an affordable option, non-nvme ssds can provide you with excellent performance and storage capabilities.
However, if you’re looking for faster speeds and higher storage capabilities, and you can afford a higher price tag, an nvme ssd is your best bet.
It can significantly improve the overall performance of your system and provide you with quicker data transfer speeds.
In the end, it all comes down to your needs and budget. Overall, both nvme and non-nvme ssds have their advantages, and choosing the right one is essential for maximizing your computer’s potential.
So, make the right choice, and enjoy a faster and smoother computing experience!