Sata Cable Right Angle Vs Left Angle Which is Better?
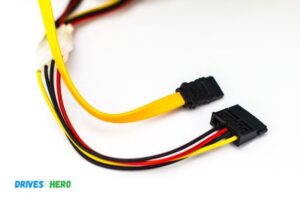
Both SATA cable right angle and left angle connectors serve the same function, but the direction in which they bend differs.
A righ tangle connector bends to the right when plugged into a drive, while a left-angle connector bends to the left.
The choice between the two primarily depends on the layout of your computer’s motherboard and where your SATA ports are located.
SATA cables with right or left angle connectors are designed to improve space management within a computer tower.
The angled connectors allow for easier routing of cables, especially in tight spaces, and can potentially enhance airflow within the system.
However, given that the only difference between them is the direction in which they bend, the choice between a right-angle and a left-angle connector will be defined by the specific configuration of your computer system.
When choosing between a right-angle and a left-angle SATA cable, it’s all about the specific needs of your computer configuration.
If your SATA ports are located such that a cable bending to the right would cause less obstruction, then a right-angle cable would be the go-to option.
Alternatively, if a cable bending to the left would be more convenient, then a left-angle cable would be the choice.
It’s all about picking the solution that best optimizes your system’s internal space and
6 Features Comparison: Sata Cable Right Angle Vs Left Angle
| Features | Sata Cable Right Angle | Sata Cable Left Angle |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Right Angle points to the right side | Left Angle points to the left side |
| Use | Ideal to connect to ports that are towards the right side of the device | Ideal for ports facing towards the left side of the device |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to right angled connection | More flexible due to left angled connection |
| Compatibility | Compatible with both SATA III and SATA II | Compatible with both SATA III and SATA II |
| Speed | Supports speeds up to 6 Gbps | Supports speeds up to 6 Gbps |
| Use Case | Mainly used in desktop computers | Mainly used in laptops or slim devices |
Key Takeaway

Five Facts About: Sata Cable Right Angle Vs Left Angle
Understanding The Basics
The difference between SATA cable right angle and left angle is an essential aspect to understand when setting up computer hardware.
Knowing their distinctions can help you optimize cable management and improve airflow within your computer system.
Evolution Of Sata Cables
- SATA cables have evolved significantly since their introduction in the early 2000s.
- The first generation of SATA cables, known as SATA 1.0, supported data transfer speeds of up to 1.5 Gbps.
- With the introduction of SATA 2.0, commonly referred to as SATA II, speeds increased to 3 Gbps.
- The latest generation, SATA 3.0 or SATA III, offers even faster speeds of up to 6 Gbps.
- The evolution of SATA cables has allowed for faster and more efficient data transfer between storage devices and motherboards.
Brief Explanation Of Sata Connectors
SATA connectors are used to connect SATA cables to storage devices and motherboards.
SATA connectors come in two main types:
The data connector and the power connector.
- The data connector, also known as the SATA data cable, is responsible for transmitting data between the storage device and the motherboard.
- The power connector, on the other hand, supplies power to the storage device, ensuring it operates correctly.
Common Types Of Sata Cables
Straight SATA Cable:
This is the most commonly used SATA cable, with connectors that are straight and do not have any angles.
Right Angle SATA Cable:
This type of SATA cable has a right-angle connector on one end, making it ideal for tight spaces where a straight connector may not fit.
Left Angle SATA Cable:
Similar to the right angle SATA cable, the left-angle SATA cable has a left-angle connector on one end.
Latching SATA Cable:
Latching SATA cables have a latch on each connector, offering a secure and reliable connection that is less likely to come loose.
SATA Power Cable:
SATA power cables are used to provide power to SATA devices, such as hard drives and SSDs.
SATA Extension Cable:
SATA extension cables are used to extend the length of an existing SATA cable, allowing for greater flexibility in cable placement.
Understanding the basics of SATA cables, including their evolution, connectors, and common types, is essential for anyone looking to build or upgrade a computer system.
Whether you need a straight cable for standard connections or a right/left angle cable for tight spaces, SATA cables offer versatility and performance.
Selecting the right SATA cable can make a significant difference in data transfer speeds and overall system functionality.
Right Angle Sata Cables: Advantages And Uses
Right angle SATA cables offer several advantages over left angle cables, including better cable management and improved airflow.
These cables are commonly used in tight spaces and provide a more organized setup for SATA devices.
When it comes to organizing the cables inside your computer or any other device, it’s essential to optimize space and ensure efficient connectivity.
One type of cable that can greatly contribute to this goal is the right angle SATA cable.
In this section, we will explore the benefits and ideal scenarios for using right angle SATA cables.
Benefits Of Right Angle Sata Cables:
Space-saving design:
Right angle SATA cables are designed with a 90-degree bend, allowing them to fit into tight spaces seamlessly.
This makes them highly convenient for systems with limited space, as they help reduce cable clutter and promote efficient airflow.
Easy cable management:
The compact and flexible nature of right angle SATA cables makes it easier to manage and route cables within your device.
Whether you’re working on a computer build, upgrading a hard drive, or connecting multiple storage devices, these cables offer a neat and organized approach.
Improved durability:
Right angle SATA cables feature a reinforced design at the connector bend, offering increased durability and reducing the risk of accidental damage.
This ensures a reliable connection while minimizing the chances of cable failure or signal loss over time.
Ideal Scenarios For Using Right Angle Sata Cables:
Compact computer builds:
If you’re constructing a small form factor computer or a compact gaming rig, space is at a premium.
Right angle SATA cables provide a practical solution by allowing you to connect storage devices in a tight space without compromising on cable management or performance.
Server racks and crowded enclosures:
Server racks and crowded enclosures often have limited space for cable management.
Right angle SATA cables alleviate this issue by offering a space-saving design that helps maintain efficient airflow and reduces clutter, making it easier to manage and maintain your server infrastructure.
Upgrading existing storage devices:
When upgrading or replacing storage devices, especially those situated in tight areas, right angle SATA cables provide the flexibility to connect new drives without strain.
Their compact design allows for hassle-free installation and easy routing within your device.
Right angle SATA cables offer numerous advantages, including their space-saving design and improved cable management.
These cables are particularly useful in compact computer builds, server racks, and when upgrading existing storage devices.
By choosing the appropriate cable for your needs, you can improve the overall organization, functionality, and lifespan of your devices.
Left Angle Sata Cables: Advantages And Uses
Left angle SATA cables offer several advantages over right angle cables, including better cable management and improved airflow within computer systems.
They are commonly used in tight spaces where traditional straight or right angle cables prove challenging to connect.
When it comes to connecting your storage devices, the type of SATA cable you choose can make a significant difference in the overall performance and organization of your system.
We will take a closer look at left angle SATA cables, examining their advantages and ideal scenarios for use.
Benefits Of Left Angle Sata Cables
Left angle SATA cables offer several benefits that can enhance the efficiency and functionality of your setup.
These advantages include:
Flexibility:
Left angle SATA cables are designed with a 90-degree left turn, which allows for a more flexible connection.
This flexibility enables easier cable routing and better cable management within your configuration.
Space-saving:
The left angle design of these cables helps save valuable space inside your system.
By angling the cable, it avoids unnecessary bends and loops that can cluster the interior and potentially obstruct airflow.
Improved airflow:
By reducing cable clutter and optimizing cable routing, left angle SATA cables promote better airflow within your system.
This improvement in airflow can assist in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating issues that may arise due to poor cable management.
Ideal Scenarios For Using Left Angle Sata Cables
Left angle SATA cables are particularly well-suited for various scenarios where space optimization and efficient cable management are essential.
These situations include:
Compact builds:
If you have a small form factor PC or a compact build where space is at a premium, left angle SATA cables can provide a compact and tidy solution.
Their angled design ensures efficient utilization of limited space, allowing for a clean and well-organized setup.
Custom water-cooling loops:
For enthusiasts who utilize custom water-cooling loops in their systems, left angle SATA cables can be an excellent choice.
Their flexible and space-saving design simplifies cable routing near water blocks and radiators, reducing the risk of cable interference.
Rack-mounted servers:
In rack-mounted server environments, where space optimization is crucial, left angle SATA cables offer a practical solution.
These cables help to maintain a clean and orderly server setup, minimizing the risk of accidental disconnections and simplifying maintenance tasks.
Left angle SATA cables provide numerous advantages when it comes to flexibility, space optimization, and efficient cable management.
Their versatility makes them an excellent choice for compact builds, custom water-cooling loops, and rack-mounted servers.
By utilizing left angle SATA cables, you can enhance the overall performance, organization, and longevity of your system.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Between Right And Left Angle Sata Cables
Factors to consider when choosing between right and left-angle SATA cables include the positioning of the connectors, space availability in the device, cable management needs, and the overall aesthetics of the setup.
The right angle cables are ideal for tight spaces, while left angle cables offer flexibility in routing and alignment. Choose the one that best suits your specific requirements.
When it comes to connecting hardware and components in your computer system, choosing the right SATA cable can make all the difference.
Whether you opt for a right angle or left angle SATA cable depends on several key factors.
In this section, we will explore the considerations to keep in mind when selecting between these two options.
Compatibility With Hardware And Components:
Right Angle SATA Cable:
- Ideal for tight spaces and cramped configurations.
- Suited for motherboards with horizontally aligned SATA ports.
- Enables easier installation in cases with limited clearance.
Left Angle SATA Cable:
- Well-suited for vertically aligned SATA ports on motherboards.
- Designed to fit in cases with more space around the SATA ports.
- Enables better airflow and reduces cable clutter.
Space Constraints And Cable Management:
Right Angle SATA Cable:
- Enables flexibility in small form factor cases.
- Helps manage cable routing and reduces strain on ports.
- Allows for efficient cable management and a cleaner setup.
Left Angle SATA Cable:
- Provides a tidy setup by routing cables downward or sideways.
- Suitable for cases with ample space for cable management.
- Minimizes the risk of cable interference with other components.
Ease Of Installation And Accessibility:
Right Angle SATA Cable:
- Simplifies the installation process in tight spaces.
- Facilitates easy connection when dealing with obstructed ports.
- Offers convenient accessibility for connecting and disconnecting devices.
Left Angle SATA Cable:
- Enables simple plug-and-play installation for easily accessible ports.
- Works well for setups with readily available SATA ports.
- Allows for hassle-free removal and replacement of SATA devices.
Considerations For Data Transfer And Performance:
Right Angle SATA Cable:
- May affect data transfer speed in some cases due to the bending angle.
- Performance impact is not significant for standard usage.
- It is essential to choose high-quality cables for optimal performance.
Left Angle SATA Cable:
- Offers a straighter path for data transfer, minimizing any potential signal interference.
- Provides consistent data transfer speed, ideal for high-performance systems.
- Ensures reliable connectivity for demanding applications.
Choosing between right angle and left angle SATA cables depends on various factors such as compatibility, space constraints, ease of installation, and performance requirements.
Consider your specific setup and needs to make an informed decision. Regardless of the angle you choose, prioritize cable quality to ensure efficient and reliable data transfer within your system.
Choosing The Right Angle For Your Setup
Choosing the right angle for your setup can make a significant difference in the efficiency and performance of your sata cable connections.
Whether it’s a right angle or left angle, selecting the appropriate option can optimize cable management and airflow within your system, ensuring hassle-free connectivity.
When it comes to setting up your computer components, choosing the right angle for your SATA cables is an important decision.
The angle of the cable can affect the overall performance and functionality of your setup.
In this section, we will discuss how to assess the layout and spacing of your components, evaluate cable routing options, and take into account future expansion or upgrades.
Assessing The Layout And Spacing Of Your Components:
Consider the location of your motherboard and hard drives:
Assess the position and orientation of these components within your computer case.
Measure the necessary cable lengths:
Determine the distance between the components to ensure the cables will reach comfortably.
Observe space restrictions:
Consider any physical or structural constraints that may affect the positioning of the SATA cables.
Note the availability of ports:
Check the number and location of SATA ports on your motherboard and drives.
Evaluating Cable Routing Options:
Identify potential cable interference:
Take note of any potential obstacles or other cables that could interfere with proper cable routing.
Choose the appropriate cable routing path:
Consider the most direct and efficient route for the SATA cables to ensure optimal performance and minimize cable clutter.
Opt for cable management solutions:
Explore cable management options such as cable ties, clips, or routing channels to keep the cables organized and secure.
Taking Into Account Future Expansion Or Upgrades:
- Consider potential future needs: Assess whether you plan to add more components or upgrade your existing ones in the future.
- Determine the flexibility required: Decide if you will need to move or rearrange your components in the future, and select appropriate cable angles accordingly.
- Plan for cable accessibility: Ensure that the SATA cables are easily accessible for future maintenance or upgrades.
By carefully assessing the layout and spacing of your components, evaluating cable routing options, and considering future expansion or upgrades, you can choose the right angle for your SATA cables to optimize the performance and functionality of your computer setup.
Take the time to plan and select the most suitable cable angles to ensure a smooth and efficient system that meets both your current and future needs.
Comparing Right And Left Angle Sata Cables: Performance And Reliability
SATA cables with right and left angle connectors differ in terms of performance and reliability.
Understanding the pros and cons of each option can help optimize your computer’s efficiency and minimize the risk of data loss.
Understanding The Impact On Signal Integrity
Right angle and left angle SATA cables play a significant role in maintaining signal integrity within computer systems.
These cables are designed to transmit data from storage devices like hard drives and solid-state drives to the motherboard, ensuring a seamless flow of information.
But how do they differ in terms of performance and reliability?
Let’s delve into the details:
Packaging signals into cables and transmitting them effectively is crucial in achieving optimal performance.
The positioning of SATA cables can influence signal integrity, and this is where the distinction between right angle and left angle cables becomes pertinent.
Right angle SATA cables are designed with a 90-degree bend, allowing for greater flexibility in cable management.
This feature helps to reduce the strain and tension on the cable, minimizing the risk of signal interference.
By enabling easy routing and providing a more compact layout, right angle cables can help maintain an organized and clutter-free system.
On the other hand, left angle SATA cables have a 180-degree bend, with the connector facing the opposite direction.
This design allows for a more streamlined cable placement, especially in tight spaces.
Left angle cables are particularly useful when dealing with limited room for cable routing.
Ultimately, both right angle and left angle SATA cables serve the same purpose of transmitting data reliably.
However, understanding their impact on signal integrity is vital to choose the right cable configuration for your specific needs.
Potential Issues And Considerations With Cable Orientation
While right angle and left angle SATA cables offer advantages in terms of cable management, it’s important to consider potential issues and limitations as well.
Here are some key considerations:
The orientation of the cable connectors can sometimes pose challenges in terms of compatibility with certain devices and system configurations.
Before purchasing SATA cables, it’s crucial to ensure that the chosen orientation is compatible with your specific hardware setup.
Right angle cables, due to their 90-degree bend, may protrude in a direction that is not optimal for certain cases or setups, causing space constraints.
It’s crucial to take into account the available space in your system enclosure and assess whether a right angle cable would be suitable.
Conversely, left angle cables with their 180-degree bend may have specific space requirements as well.
Depending on the position of SATA ports on the motherboard and the dimensions of your case, it’s important to evaluate whether left angle cables will fit properly and allow for smooth cable routing.
Another consideration is the impact of cable orientation on airflow within the system.
Improper cable management can impede the flow of air, leading to increased temperatures and potentially affecting system performance.
Therefore, it’s essential to carefully plan cable routing to ensure optimal cooling.
By taking these potential issues into account and considering the available space, compatibility, and airflow requirements, you can make an informed decision when choosing between SATA cable orientations.
Real-World Tests And User Experiences
Understanding the practical implications of SATA cable orientation is essential, and real-world tests and user experiences can provide valuable insights.
Here are some observations from individuals who have tested and utilized both right angle and left angle SATA cables:
In terms of performance, many users report no significant difference between right angle and left angle cables, indicating that both orientations offer reliable data transmission.
SATA cables, regardless of their angle, are capable of providing the necessary connectivity for standard usage scenarios.
However, the suitability of a specific cable orientation often depends on the individual’s system layout and cable management requirements.
Users who prioritize space-saving and tidy cable arrangements often favor right angle cables for their flexibility in routing and ease of cable management.
Conversely, users with restricted space or specific case designs that require vertically aligned cables find left angle SATA cables more suitable.
These cables can facilitate a cleaner and neater cable routing path, especially in compact or specialized enclosures.
Ultimately, the choice between right angle and left angle SATA cables depends on your specific needs, space constraints, and cable management preferences.
Real-world tests and user experiences highlight the importance of considering these factors and selecting the cable orientation that best accommodates your unique setup.
By understanding the impact on signal integrity, potential issues, and real-world experiences, you can make an informed decision when choosing between right angle and left angle SATA cables for your computer system.
Whether you prioritize cable management, compatibility, or space-saving, weighing these factors will help ensure an optimal and reliable data transmission solution.
Best Practices For A Reliable Sata Cable Connection
Looking for the best SATA cable connection? Choose between a SATA cable with a right angle or left angle to ensure reliability and efficiency.
SATA cables play a crucial role in connecting your hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) to your computer.
To ensure a reliable data transfer and prevent potential issues, it is essential to follow best practices for handling and managing SATA cables.
This section will guide you through the proper cable handling, ensuring secure connections, and troubleshooting common issues.
Proper Cable Handling And Management:
Inspect the cable:
Before connecting the SATA cable, take a moment to inspect it for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires or bent connectors.
Orient the connectors:
When attaching the SATA cable, ensure that you align the connectors correctly with the corresponding ports on both the drive and the motherboard.
This prevents any misalignment and potential damage to the connectors.
Avoid tight bends:
SATA cables should not be excessively bent or twisted, as this can lead to signal loss or damage over time.
Use gentle curves and avoid sharp angles to maintain the cable’s integrity.
Adequate cable length:
Choose an appropriate cable length to avoid unnecessary tension or strain on the connectors.
A longer cable allows flexibility while routing and managing the cables inside your computer case.
Ensuring Secure Connections And Avoiding Damage:
Firm and secure connections:
Make sure to firmly push the connectors into their respective ports until you hear a click.
A loose connection can lead to data transfer errors or intermittent connectivity issues.
Use locking mechanisms:
Some SATA cables come with locking mechanisms, such as clips or latches.
Engage these mechanisms to ensure a secure connection that won’t accidentally disconnect, particularly in high-vibration environments.
Avoid excessive force:
While it’s important to have a secure connection, avoid using excessive force when connecting or disconnecting SATA cables.
Applying too much pressure can potentially damage the connectors, leading to distorted or weakened signals.
Tips For Troubleshooting Common Issues:
Securely reseat the cables:
If you encounter intermittent connectivity or data transfer issues, try reseating the SATA cables on both the drive and motherboard ends. Sometimes, a loose connection could be the cause of the problem.
Check for bent pins:
Inspect the SATA connectors for any bent or missing pins. If you notice any abnormalities, gently straighten them with a pair of tweezers. Be cautious to not cause further damage.
Try different ports:
If a particular SATA port is causing problems, try using a different port on the motherboard.
This can help determine if the issue lies with the cable or the port itself.
Consider cable replacement:
If all else fails and you have exhausted troubleshooting options, it may be time to replace the SATA cable.
Damage or wear over time can affect cable performance, and a new cable might resolve the issue.
By following these best practices for handling, connecting, and troubleshooting SATA cables, you can ensure a reliable and secure data transfer between your storage devices and your computer.
Implement these techniques to maintain optimal performance and prevent unnecessary data loss.
FAQ About Sata Cable Right Angle Vs Left Angle
What is the Difference between a Right Angle Sata Cable And a Left Angle Sata Cable ?
A right angle Sata cable is bent at a 90-degree angle near the end of the connector, which allows for easier connections in tight spaces.
A left angle Sata cable is bent at a 270-degree angle near the end of the connector, which also allows for easier connection in tight spaces but from different angles than the right angled cable.
Is One Type of Sata Cable Better Than the Other for Certain Applications ?
Yes, one type of SATA cable may be better than the other for certain applications.
For example, a Serial ATA III (SATA 3) cable is typically faster and more reliable than a Serial ATA II (SATA 2) cable for data transfers, making it preferable for high-performance applications.
How Do I Know Which Type of Sata Cable to Use for My Specific Setup ?
The type of SATA cable to be used for a specific setup depends on the type of SATA interface that is available in the system.
The most common types are Serial ATA (SATA) and eSATA. It is important to check the device manual or specifications before purchasing a new SATA cable.
Are There Any Compatibility Issues With Using Either a Right Or Left Angle Sata Cable in Different Systems ?
Yes, there are compatibility issues with using either a right or left angle SATA cable in different systems.
Right-angle cables can be difficult to fit into tight spaces, while left-angle cables may not fit at all. Additionally, some motherboards only accept one type of connector and won’t work with the other type.
Conclusion
To sum it up, while both SATA cables with right angle and left angle connectors serve the same purpose of connecting storage devices to the motherboard, they differ in terms of space efficiency and cable management.
The right angle SATA cable is ideal for tight spaces as it enables a more compact and streamlined setup, reducing cable clutter.
On the other hand, the left angle SATA cable is advantageous when you need to connect drives located vertically or in a position where a right angle connector would not fit comfortably.
Ultimately, your choice between the two will depend on your specific hardware setup and space constraints.
Regardless of the angle you choose, ensure that you select a high-quality SATA cable that meets the necessary data transfer speeds for optimal performance.
With the right cable, you can enhance the reliability and functionality of your storage devices.