Ssd Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc: Which Is The More Favorable Option?
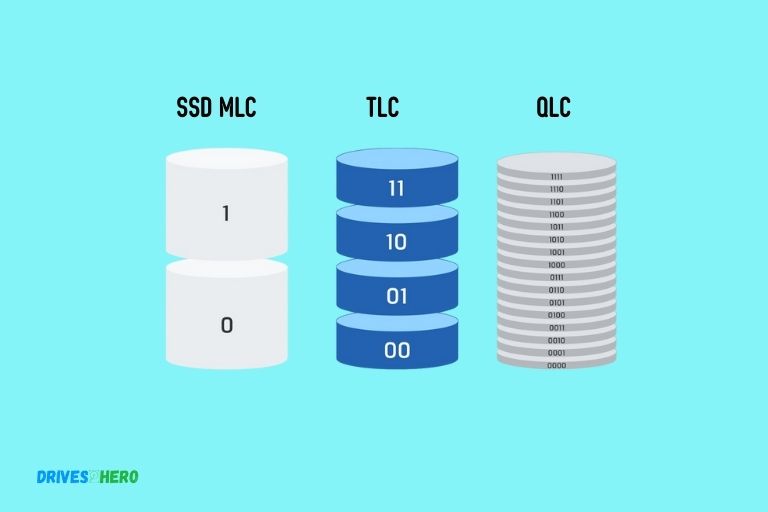
In comparison, MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs are more durable and faster in terms of writing speed than TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs, which store three bits per cell.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs, on the other hand, store four bits per cell but come with slower write speeds and less durability compared to both MLC and TLC.
MLC, TLC, and QLC are types of NAND flash memory used in solid-state drives (SSDs). MLC is a type of memory that can store more than one bit of information per cell, making it faster and more durable.
It is typically used in high-end storage devices. TLC stores three bits per cell and is slower and less durable than MLC, but it tends to be cheaper, making it popular for consumer-grade devices. QLC stores four bits per cell, which makes it even cheaper than TLC but at the cost of durability and speed.
Key Takeaway
Ssd Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc – Which Is Faster?
Comparing Ssd Mlc, Tlc, and Qlc, the speed varies, with Mlc SSDs being the fastest, followed by Tlc and then Qlc SSDs.
Their performance differs due to variations in their memory cell structure and technology. If you’re in the market for a new SSD (Solid State Drive), you may have come across terms like MLC, TLC, and QLC.
Comparison Of Read And Write Speeds For Each Type:
MLC (Multi-Level Cell):
- Read Speed: MLC SSDs tend to have faster read speeds compared to TLC and QLC SSDs. This means that accessing data stored on an MLC SSD is generally quicker, resulting in faster boot times and overall system responsiveness.
- Write Speed: MLC SSDs also typically offer faster write speeds than TLC and QLC SSDs. This makes them well-suited for tasks that involve intensive write operations, such as running virtual machines or editing large files.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell):
- Read Speed: While TLC SSDs may not match the read speeds of MLC SSDs, they still deliver impressive performance. You can expect smooth and snappy operation when accessing data on a TLC SSD.
- Write Speed: TLC SSDs usually have slightly lower write speeds compared to MLC SSDs. However, for everyday computing tasks like web browsing, multimedia streaming, and gaming, TLC SSDs provide more than enough speed.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell):
- Read Speed: QLC SSDs offer decent read speeds, although they may be slightly slower compared to MLC and TLC SSDs. Nonetheless, you can still enjoy quick data access for general computing tasks.
- Write Speed: QLC SSDs generally have lower write speeds compared to MLC and TLC SSDs. They are better suited for regular PC usage where heavy write workloads aren’t common.
Factors Impacting Performance And Real-World Implications:
Controller: The SSD controller plays a crucial role in determining the overall speed and performance of the drive. A well-designed controller can optimize the read and write speeds of NAND flash memory, improving the overall efficiency of the SSD.
NAND Flash Memory: The type and quality of NAND flash memory used in an SSD can significantly impact its speed. While MLC offers the fastest performance overall, advancements in TLC and QLC technology have closed the gap, providing impressive speeds for everyday use.
Workload Type: The type of workload you typically perform on your system will affect the perceived speed of the SSD. Tasks that involve heavy read/write operations, such as video editing or data analysis, will benefit more from the faster speeds of MLC or TLC SSDs.
Operating System and Applications: The efficiency and optimization of your operating system and applications can also influence the real-world performance of your SSD. Well-optimized software can leverage the full potential of the SSD, ensuring smooth and responsive system performance.
When comparing SSDs based on their read and write speeds, MLC SSDs tend to offer the fastest performance, followed by TLC and QLC SSDs.
Ssd Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc – Which Is More Durable?
SSD MLC, TLC, and QLC are all types of solid-state drives. MLC offers a higher durability compared to TLC and QLC due to its more advanced technology and higher write endurance.
Comparison Of Endurance Ratings And Lifespan:
MLC SSDs:
- Typically have the highest endurance ratings among the three types.
- Endurance ratings are specified in Terabytes Written (TBW) and indicate the amount of data that can be written to the drive before it fails.
- MLC SSDs can endure tens of thousands of write cycles, making them suitable for heavy workload scenarios such as enterprise environments where constant data writing is required.
Lifespan:
- MLC SSDs have a longer lifespan compared to TLC and QLC SSDs.
TLC SSDs:
- Have a lower endurance rating than MLC SSDs but are still suitable for most consumer applications.
- Endurance ratings for TLC SSDs are usually around one-third or one-fourth of the MLC SSDs.
- While TLC SSDs are less durable than MLC SSDs, they still provide sufficient endurance for typical day-to-day use, including gaming, multimedia, and general computing tasks.
Lifespan:
- Although TLC SSDs have a shorter lifespan than MLC SSDs, they can still easily last for several years, even with intensive use.
QLC SSDs:
- Offer the lowest endurance rating of the three types.
- Endurance ratings for QLC SSDs are generally lower than both MLC and TLC SSDs.
- While QLC SSDs may not be the ideal choice for heavy write-intensive applications, they are perfectly suitable for light to moderate usage scenarios, such as regular personal computing and storing media files.
Lifespan:
- QLC SSDs may have a shorter lifespan compared to MLC and TLC SSDs, but with normal usage, they can still last for a considerable amount of time.
Impact Of Write Cycles And Data Retention:
MLC SSDs:
- With their higher endurance, MLC SSDs can handle a significantly higher number of write cycles compared to TLC and QLC SSDs.
- MLC SSDs also have better data retention capabilities, ensuring the stored data remains intact for more extended periods.
TLC SSDs:
- Although TLC SSDs have a lower endurance rating, they still provide ample write cycles for most consumer applications.
- Data retention is slightly lower compared to MLC SSDs, but still reliable over typical usage durations.
QLC SSDs:
- QLC SSDs have the lowest endurance and may wear out faster with intensive data writing.
- However, they still offer sufficient write cycles for regular personal computing needs.
- QLC SSDs’ data retention is slightly compromised compared to MLC and TLC SSDs, but they are perfectly suitable for non-critical data storage purposes.
The durability of an SSD depends on the specific type you choose. MLC SSDs exhibit the highest endurance and longest lifespan, making them ideal for heavy workload scenarios.
Evaluating Ssd Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc – Which Is More Cost-Effective?
Comparing SSD MLC, TLC, and QLC reveals which option is more cost-effective. This analysis helps determine the best choice based on efficiency and savings.
Comparison Of Cost Per Gigabyte For Each Type:
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of SSDs, it’s essential to compare the cost per gigabyte for MLC, TLC, and QLC drives.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs:
- MLC drives are known for their high performance and durability, making them ideal for professional use.
- They utilize a two-bit cell, allowing for faster read and write speeds.
- MLC SSDs typically have a higher cost per gigabyte compared to other types, due to their advanced technology and superior performance.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs:
- TLC drives are designed to strike a balance between cost and performance.
- They utilize a three-bit cell, offering higher storage capacity than MLC drives.
- The cost per gigabyte of TLC SSDs is generally lower compared to MLC, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs:
- QLC drives are the most affordable option among the three types.
- They utilize a four-bit cell, offering even higher storage capacity than both MLC and TLC drives.
- While QLC SSDs provide a budget-friendly option, it’s important to note that they typically have slower transfer speeds and a shorter lifespan.
By understanding the differences in cost per gigabyte among MLC, TLC, and QLC SSDs, you can make an informed decision based on your storage needs and budget considerations. Remember, it’s crucial to strike a balance between storage requirements and affordability when choosing an SSD.
Choosing The Right Ssd Type For Your Needs
Choosing the right SSD type for your needs can be a daunting task. MLC, TLC, and QLC are the three main types of SSDs available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s dive into some recommendations based on use cases and factors to consider when selecting an SSD type:
Recommendations Based On Use Cases
Gaming:
- Speed is paramount for gaming, as it reduces load times and improves overall gaming experience.
- Opt for an SSD with high read and write speeds, such as an MLC or TLC SSD.
- Look for models with ample storage capacity to accommodate game installations.
- Consider NVMe SSDs for even faster performance.
Productivity (E.G., Office Work, Content Creation):
- Storage space is crucial for productivity tasks that involve working with large files.
- A TLC or QLC SSD with a larger storage capacity would be suitable for storing documents, images, videos, and other work-related files.
- Opt for an SSD with good write speeds to ensure efficient file saving and data transfer.
Multimedia (E.G., Photo Editing, Video Rendering):
- Multimedia tasks often require both high storage capacity and fast performance.
- Consider an MLC or TLC SSD with a combination of high read and write speeds.
- Look for larger storage capacities to store multimedia files, especially if you work with high-resolution images or videos.
General Use (E.G., Web Browsing, Everyday Tasks):
- For general use, including web browsing and everyday tasks, a TLC or QLC SSD would suffice.
- Look for an SSD with an adequate storage capacity for your needs.
- Consider the price-to-performance ratio to get the best value for your money.
Factors To Consider When Selecting An Ssd Type
Performance:
- Consider the SSD’s read and write speeds, as well as its random read and write speeds.
- Higher speeds generally result in snappier performance and faster data transfer.
Endurance:
- Different SSD types have varying endurance levels due to the number of program-erase cycles they can endure.
- MLC SSDs have the highest endurance, followed by TLC and then QLC SSDs.
- Consider your workload and how frequently you expect to write data to determine the appropriate endurance level for your needs.
Price:
- SSD prices vary depending on the type and capacity.
- MLC SSDs tend to be more expensive, followed by TLC and QLC SSDs, which are generally more budget-friendly.
- Consider your budget and the required storage capacity to make an informed decision.
Remember to carefully evaluate your specific requirements and use cases when selecting an SSD type. By considering factors such as performance, endurance, and price, you can choose the right SSD that will meet your needs and provide an optimal computing experience.
Which Type of SSD (MLC, TLC, or QLC) is the Best Option?
When it comes to choosing the best type of SSD, understanding the difference between QLC and TLC SSD is crucial. QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs offer larger storage capacities at a more affordable price, but may sacrifice some performance and endurance. On the other hand, TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs provide faster speeds and longer lifespan, but with a slightly higher cost. Ultimately, the best option depends on individual needs, budget, and desired performance. Choose wisely, keeping in mind the difference between QLC and TLC SSD.
Making An Informed Decision For Your Ssd
Making an informed decision for your SSD requires understanding the differences between MLC, TLC, and QLC. These variations impact performance, durability, and cost, and considering these factors will help you choose the right SSD for your needs.
Recap Of The Key Differences Between Mlc, Tlc, And Qlc Ssds
MLC, TLC, and QLC are all different types of SSD (Solid State Drive) technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. To make an informed decision on which SSD to choose, it’s important to understand these differences.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs:
- Utilizes a two-level cell structure to store data.
- Offers better performance and endurance compared to TLC and QLC.
- Provides higher read/write speeds, making it suitable for demanding workloads.
- Generally more expensive due to the advanced technology used.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs:
- Uses a three-level cell structure to store data.
- Provides a balance between performance, endurance, and cost.
- Offers higher storage capacities at more affordable prices.
- Slightly slower read/write speeds compared to MLC.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs:
- Employs a four-level cell structure to store data.
- Offers higher storage capacities at even more affordable prices.
- Provides lower endurance and slower performance compared to MLC and TLC.
- Suitable for mainstream users with average storage needs.
Final Thoughts On Selecting The Best Ssd Type For Your Requirements
Here are some points to consider:
Determine your workload: Assess the nature of your tasks and the level of performance you require. If you work with large files or demanding applications, consider MLC or TLC SSDs for faster read/write speeds.
Consider budget and storage needs: If you’re on a tight budget or require a larger storage capacity, QLC SSDs might be a suitable option. They provide more affordable pricing with higher storage capacities.
Evaluate endurance requirements: If you need an SSD for heavy workloads or constant data writing, MLC SSDs offer better endurance compared to TLC and QLC. If you’re a casual user who doesn’t require extensive data writing, TLC or QLC SSDs can still provide satisfactory performance.
Seek expert advice: If you’re still unsure which SSD type to choose, consult professionals or read trusted reviews and comparisons. They can provide valuable insights based on your specific requirements.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to SSDs. Your choice should be based on a careful evaluation of your workload, budget, storage needs, and endurance requirements.
Conclusion
After comparing SSD MLC, TLC, and QLC, it is evident that each has its own strengths and weaknesses. MLC provides exceptional performance and endurance, making it ideal for demanding applications. TLC strikes a balance between cost and performance.
QLC, while cost-effective, sacrifices some performance and durability. When choosing between these options, it is important to consider your specific needs.
If you require high-speed data transfers and extended endurance, MLC is the way to go. TLC offers a good compromise between performance and cost, making it suitable for general use.
Finally, QLC provides an economical solution for consumers concerned with budget constraints. Ultimately, the decision boils down to your requirements and budget.






