Datacenter Ssd Vs Nvme Ssd: Which One Better For You!
Data Center SSD and NVMe SSD are both forms of solid-state drives that are used for storage in computing.
While both are SSDs, they differ in several ways. Data Center SSDs are designed for use in high-availability environments, offering features like power-loss protection and end-to-end data protection.
NVMe SSDs, on the other hand, leverage the NVMe interface to provide greater throughput and lower latency, making them ideal for applications that require fast and efficient data processing.
Data Center SSDs are optimized for use in server environments where reliability, sustained performance, and data integrity are paramount.
They often include features like enhanced power-loss data protection and end-to-end data path protection.
NVMe SSDs are a newer type of SSD that use the NVMe interface, which was specifically designed for flash storage.
It offers faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to other SSDs, making it ideal for high-performance computing environments.
Data Center SSDs and NVMe SSDs both serve critical roles in modern computing environments. While they both offer solid-state storage, their different features make them suitable for different applications.
It’s essential to understand these differences to choose the right SSD for your specific needs. Whether it’s the enhanced data protection of a Data Center SSD or the fast data
8 Comparison: Datacenter SSD vs NVMe SSD
| Feature | Datacenter SSD | NVMe SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Lower than NVMe SSD | Up to 6 times faster than Datacenter SSD |
| Price | Typically cheaper | More expensive |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | Designed for long term use | Typically less durable than Datacenter SSD |
| Capacity | Higher capacity (up to 16 TB) | Lower capacity (up to 4TB) |
| Interface | SATA, SAS | PCIe |
| Use Case | Ideal for datacenters and heavy workloads | Ideal for personal, gaming and high-performance computing |
Key Takeaway

Five Facts About: Datacenter SSD vs NVMe SSD
Understanding The Difference Between Datacenter Ssd And Nvme Ssd
Datacenter SSD and NVMe SSD are two types of storage devices used in datacenters. While both offer high-performance storage, NVMe SSDs are faster and more efficient due to their direct connection to the PCIe bus.
Understanding the differences between these two options is crucial for optimizing datacenter storage solutions.
Datacenters are critical infrastructures that require storage solutions capable of handling vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently.
Two popular options for datacenter storage are Datacenter SSD and NVMe SSD.
Let’s explore their characteristics and features to understand their differences better:
Exploring The Characteristics And Features Of Datacenter Ssds:
Datacenter SSDs, or Solid State Drives, are a type of flash storage designed explicitly for datacenter environments.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Enhanced reliability and durability: Datacenter SSDs are built to withstand the demanding nature of datacenter operations, ensuring maximum uptime and minimizing data loss.
- High write endurance: These SSDs offer robust write endurance, allowing them to handle an extensive number of write operations without performance degradation.
- Large storage capacity: Datacenter SSDs provide substantial storage capacities, enabling datacenters to store massive volumes of data without compromising speed.
- Efficient power consumption: Designed to optimize power efficiency, datacenter SSDs can significantly reduce energy consumption, resulting in lower operational costs.
- Advanced error correction mechanisms: Datacenter SSDs incorporate advanced error correction mechanisms, enhancing data integrity and preventing data corruption.
Unraveling The Benefits And Limitations Of Nvme Ssds For Datacenter Environments:
NVMe SSDs, or Non-Volatile Memory Express Solid State Drives, represent the next generation of storage technology.
Let’s delve into their benefits and limitations in datacenter settings:
Lightning-fast data transfer speeds:
NVMe SSDs leverage the PCIe interface, delivering significantly faster data transfer rates compared to traditional datacenter SSDs.
This can greatly accelerate data processing and improve overall system performance.
Low latency:
NVMe SSDs boast exceptionally low latency, reducing the time it takes to access stored data. This directly contributes to improved responsiveness and quicker data retrieval.
Improved scalability:
Due to their efficient design, NVMe SSDs can easily scale to accommodate increasing data requirements, making them an ideal choice for datacenters seeking future-proof solutions.
Restricted compatibility:
While NVMe SSDs offer impressive performance gains, their compatibility with legacy systems might be limited, requiring infrastructure upgrades to fully harness their benefits.
Higher cost:
NVMe SSDs tend to be relatively more expensive compared to traditional datacenter SSDs.
Datacenters must consider their budget constraints before opting for NVMe technology.
Understanding the characteristics and features of both datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs is crucial for making informed decisions.
Datacenter SSDs provide reliability, durability, high storage capacity, and efficient power consumption, while NVMe SSDs offer lightning-fast speeds, low latency, improved scalability, albeit at a higher cost and potential compatibility limitations.
Choosing the right storage solution depends on the specific needs and priorities of the datacenter.
Performance And Speed Comparison: Datacenter Ssd Vs Nvme Ssd
In a performance and speed comparison, Datacenter SSD and NVMe SSD are pitted against each other.
Find out the key differences between these two storage solutions:
Datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs are both popular storage options for datacenters. Each type has its own unique characteristics and advantages.
In this section, we will analyze the performance and speed of these two types of SSDs to help you understand which one might be the best fit for your datacenter applications.
Analyzing The Read And Write Speeds Of Datacenter Ssds:
- Datacenter SSDs are known for their impressive read and write speeds, making them capable of handling heavy workloads efficiently.
- These SSDs offer fast data access and retrieval, ensuring quick response times for applications and minimizing latency.
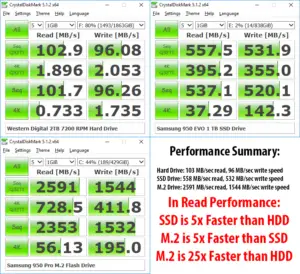
- With read speeds reaching up to 550 MB/s and write speeds up to 520 MB/s, datacenter SSDs provide reliable and fast data transfer rates.
- Their high IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) enable faster data processing, making them ideal for demanding workloads and applications.
Evaluating The Performance Benchmarks Of Nvme Ssds In Datacenter Applications:
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs take datacenter storage performance to the next level.
- This newer technology leverages the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface to achieve blazing-fast data transfer speeds.
- With read and write speeds significantly higher than traditional datacenter SSDs, NVMe SSDs can reach speeds of over 3000 MB/s, enhancing overall system performance.
- The increased bandwidth and reduced latency of NVMe SSDs make them perfect for data-intensive tasks and high-performance computing.
- These SSDs excel in environments where fast data access, low latency, and high IOPS are critical, such as big data analytics, real-time data processing, and virtualization.
Both datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs deliver impressive performance and speed. While datacenter SSDs offer excellent read and write speeds, NVMe SSDs take it a step further with their superior performance benchmarks.
When choosing between the two, consider the specific requirements of your datacenter applications and the level of performance needed.
Reliability And Endurance: Datacenter Ssd Vs Nvme Ssd
Datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs offer reliability and endurance for high-performance storage solutions.
With superior speed and durability, these storage options are ideal for data-intensive applications in a professional setting.
Assessing The Durability And Lifespan Of Datacenter Ssds
In the fast-paced world of datacenters, the reliability and endurance of storage devices are critical for seamless operations.
When it comes to datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs, understanding their reliability and endurance features is crucial in making informed decisions.
Let’s take a closer look at the durability and lifespan of these two SSD types:
Datacenter Ssds:
- Datacenter SSDs are known for their robust construction and superior endurance, making them ideal for heavy workloads.
- These SSDs are designed to withstand constant data writes and intensive operations without compromising performance.
- Key features that enhance reliability include power-loss protection, advanced error correction algorithms, and wear-leveling technologies.
- With their longer lifespan, datacenter SSDs offer businesses the peace of mind they need for uninterrupted operations.
- The MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) of datacenter SSDs is significantly higher compared to consumer-grade SSDs.
- Typically, datacenter SSDs have higher capacities and a higher number of drive writes per day (DWPD) rating, ensuring longevity.
Nvme Ssds In Datacenter Use Cases:
- NVMe SSDs bring a new level of speed and efficiency to datacenters, but they also offer impressive reliability features.
- These SSDs utilize advanced error correction technologies and thermal throttling mechanisms to prevent data loss and mitigate overheating risks.
- The incorporation of power-loss protection ensures data integrity during sudden power outages or failures.
- NVMe SSDs, with their streamlined architecture and reduced latency, offer exceptional endurance for data-intensive applications.
- With a focus on improving scalability, NVMe SSDs allow seamless expansion of storage capacity to keep up with growing data demands.
- The MTBF of NVMe SSDs is comparable to that of datacenter SSDs, further highlighting their reliability.
Both datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs bring reliability and endurance to the table, albeit with slightly different features and strengths.
Datacenter SSDs excel in heavy workloads and provide peace of mind with their longer lifespan, while NVMe SSDs offer impressive speed, scalability, and reliability for data-intensive applications in the datacenter environment.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on specific use cases and the performance requirements of the datacenter.
FAQ About Datacenter Ssd Vs Nvme Ssd
What is the difference between a datacenter SSD and a NVMe SSD?
A datacenter SSD is a type of solid-state drive (SSD) designed for use in a data center environment.
It typically offers larger capacity and higher performance than traditional HDD storage, and consumes less power.
A NVMe SSD is an even faster type of solid-state drive that utilizes the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol.
NVMe SSDs offer significantly higher performance and lower power consumption than traditional datacenter SSDs.
What are the benefits of using a datacenter SSD instead of a NVMe SSD?
Datacenter SSDs offer larger capacity and higher performance than traditional HDD storage, while consuming less power. They are also more cost-effective than NVMe SSDs, which offer significantly higher performance but are more expensive.
What are the advantages of using a NVMe SSD instead of a datacenter SSD?
NVMe SSDs offer significantly higher performance and lower power consumption than traditional datacenter SSDs. They also provide higher I/O speeds for more demanding applications.
What are the advantages of using a datacenter SSD?
The advantages of using a datacenter SSD include improved storage performance, increased reliability, and enhanced energy efficiency.
Datacenter SSDs offer faster read and write speeds than traditional SSDs, allowing for faster data access and retrieval.
They also offer higher levels of durability, due to their improved design and the fact that they are specifically designed for use in enterprise-level datacent
Conclusion
It is clear that both datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs offer significant advantages when it comes to storage performance and efficiency.
However, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your datacenter environment before making a decision. If your workload demands low latency and high bandwidth, NVMe SSDs are the ideal choice due to their faster speeds and lower latency.
On the other hand, if cost-effectiveness and reliability are of utmost importance, datacenter SSDs provide a more affordable and stable solution.
Ultimately, the key to optimizing your datacenter’s storage infrastructure lies in understanding your unique needs and finding the right balance between performance, cost, and reliability.
By carefully evaluating the benefits and drawbacks of both options, you can make an informed decision that ensures smooth datacenter operations and meets the demands of your business. Datacenter SSDs are designed for use in servers and other high-performance computing applications.
They offer excellent performance and reliability, but they’re also more expensive than other types of SSDs.
NVMe SSDs are newer than datacenter SSDs and are designed for use in consumer laptops and PCs. They offer similar performance to datacenter SSDs, but they’re much cheaper.
There’s a lot of confusion out there about the differences between datacenter SSDs and NVMe SSDs. Let’s clear things up.
Datacenter SSDs are designed for high-end enterprise applications that require the highest levels of performance and reliability.
They’re usually more expensive than consumer-grade SSDs, but they offer much higher speeds and lower latency.
NVMe SSDs are the newest type of SSD on the market, and they offer even higher performance than datacenter SSDs.
However, they’re also more expensive, so they’re not necessarily the best choice for everyone.