Ssd Tlc Vs Mlc Vs Slc: Which Is The Superior Choice?
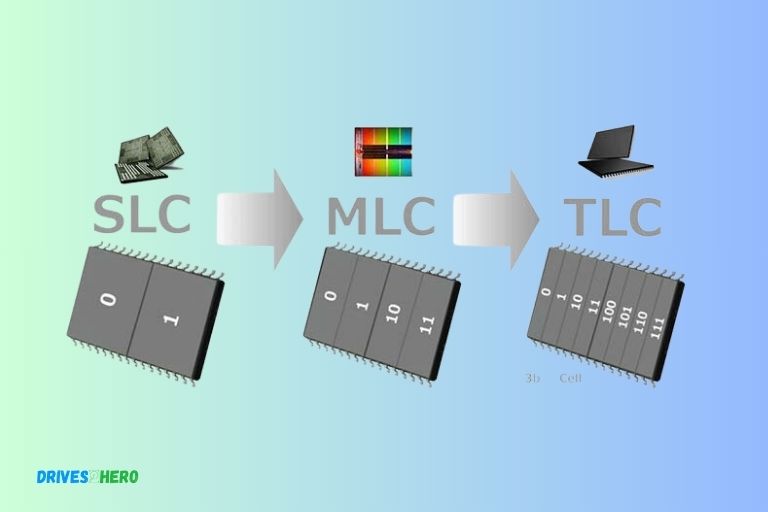
SLC, MLC, and TLC are different types of NAND flash memory used in SSDs. SLC (Single-level cell) stores one bit of data per memory cell, MLC (Multi-Level Cell) stores two bits, and TLC (Triple-Level Cell) stores three.
SLC is considered the most reliable and durable but is also the most expensive. MLC is a balance between cost and reliability, while TLC is the most affordable but has lower endurance.
SLC, MLC, and TLC refer to the number of bits stored in each cell. SLC, with one bit per cell, has the highest endurance, fastest write speeds, and greatest reliability, but at a much higher cost.
MLC, storing two bits per cell, reduces cost while still offering good performance and reliability. TLC, storing three bits per cell, is even more cost-effective, but at the expense of lower write endurance and slower write speeds.
Key Takeaway
Performance And Endurance Comparison
Performance and endurance of SSDs can be compared through different types of memory cells: TLC, MLC, and SLC. Each type has its pros and cons, impacting the speed and lifespan of the drive.
Performance Differences Between Tlc, Mlc, And Slc Ssds
SSDs (Solid State Drives) are essential components for ensuring optimal performance in modern computing devices.
They provide faster data access compared to traditional hard drives, contributing to quicker application launches and reduced boot times. When it comes to SSDs, three primary types stand out: TLC, MLC, and SLC.
Understanding the performance and endurance variations between these types is crucial in making an informed purchasing decision. Let’s dive deeper into the performance differences between TLC, MLC, and SLC SSDs.
Read And Write Speeds:
TLC (Triple-Level Cell):
- Read and write speeds are generally slower compared to MLC and SLC SSDs.
- Suitable for everyday computing tasks, such as web browsing and document editing.
- Ideal for budget-conscious consumers who prioritize affordability over extreme performance.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell):
- Offers improved read and write speeds compared to TLC SSDs.
- Well-suited for a wide range of applications, including gaming and multimedia tasks.
- Strikes a balance between performance and affordability.
SLC (Single-Level Cell):
- Exhibits the fastest read and write speeds among the three types.
- Ideally suited for demanding applications that require top-notch performance, such as professional video editing or high-performance gaming.
- Comes at a higher price point due to the enhanced performance it provides.
Random And Sequential Performance:
TLC SSDs:
- Performs well in sequential read and write operations, making it suitable for large file transfers and video editing tasks.
- Random read and write speeds are relatively lower compared to MLC and SLC SSDs.
MLC SSDs:
- Provides improved random read and write speeds compared to TLC SSDs.
- Excellent for multitasking, efficiently handling various tasks including virtual machine usage and content creation.
SLC SSDs:
- Offers the highest random read and write speeds among the three types.
- Ideal for scenarios where instantaneous data access is crucial, like enterprise-grade databases or server environments.
Latency:
TLC SSDs:
- Generally exhibits higher latency compared to MLC and SLC SSDs.
- Latency refers to the delay between initiating a data transfer and the actual transfer taking place.
- Despite the higher latency, it still delivers acceptable performance for everyday tasks.
MLC SSDs:
- Displays lower latency compared to TLC SSDs.
- Offers improved responsiveness and lower waiting times for data retrieval.
SLC SSDs:
- Boasts the lowest latency among the three types.
- Enables near-instantaneous access to data, resulting in enhanced system responsiveness and reduced waiting times.
Endurance Comparison Between Tlc, Mlc, And Slc Ssds:
Program/Erase Cycles:
TLC SSDs:
- Typically have the lowest endurance, with a limited number of program/erase (P/E) cycles.
- P/E cycles refer to the number of times data can be written and erased on the SSD before it starts experiencing performance degradation.
- Suitable for regular consumer use, but may not be ideal for sustained heavy workload or write-intensive tasks.
MLC SSDs:
- Offers higher endurance compared to TLC SSDs, with increased P/E cycles.
- Provides a better option for general consumer use and moderate workload applications.
SLC SSDs:
- Exhibits the highest endurance, with significantly more P/E cycles compared to TLC and MLC SSDs.
- Ideal for heavy workload scenarios, such as enterprise environments or servers, where constant writing and erasing of data take place.
Data Retention:
TLC SSDs:
- Typically have a slightly lower data retention period compared to MLC and SLC SSDs.
- Data retention refers to the ability of an SSD to retain stored data without degradation over time.
- Suitable for regular consumer use without extended periods of data storage.
MLC SSDs:
- Offers better data retention compared to TLC SSDs.
- Safely stores data for longer durations, making it suitable for most consumer and professional use cases.
SLC SSDs:
- Provides the highest data retention period among the three types of SSDs.
- Ensures data integrity and long-term storage reliability, ideal for critical data storage needs.
Understanding the performance and endurance variations between TLC, MLC, and SLC SSDs allows you to select the most suitable SSD for your specific needs.
Whether it’s for everyday computing, high-performance applications, or heavy workloads, choosing the right SSD ensures optimal performance and durability for your system.
Price And Capacity Considerations
The considerations for SSDs’ price and capacity depend on the type of memory cells used: TLC, MLC, or SLC. Each type offers varying levels of affordability, storage capacity, and endurance, making it essential to evaluate these factors before making a decision.
Price Differences Between Tlc, Mlc, And Slc Ssds
When it comes to price, TLC, MLC, and SLC SSDs can differ significantly.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell):
Affordable:
- TLC SSDs usually offer the lowest price per gigabyte.
- Ideal for budget-conscious buyers looking for cost-effective storage solutions.
- Higher capacities can be obtained at a reasonable price.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell):
Moderately priced:
- MLC SSDs fall in the mid-range of price per gigabyte.
- Strikes a balance between cost and performance.
- Suitable for those who require better endurance and reliability compared to TLC.
SLC (Single-Level Cell):
Expensive:
- SLC SSDs tend to have the highest price per gigabyte.
- Offers exceptional performance and durability.
- Ideal for demanding applications that require fast and reliable storage.
Cost Per Gigabyte
Determining the cost per gigabyte is essential to ensure value for money.
Here’s a breakdown of the cost per gigabyte for each SSD type:
TLC:
- Offers the most cost-effective solution, as it provides higher capacities at a relatively lower price.
- However, the tradeoff is reduced endurance compared to MLC and SLC.
MLC:
- Falls between TLC and SLC in terms of cost per gigabyte.
- Provides a good balance between capacity, endurance, and price.
- Suitable for users who prioritize a balance between performance and affordability.
SLC:
- Commands the highest cost per gigabyte.
- Provides superior endurance and reliability, but at a premium price point.
- Recommended for professional users who require the highest level of performance and reliability.
Capacity Options For Tlc, Mlc, And Slc Ssds
When it comes to capacity options, here are the maximum and minimum capacities available for each SSD type:
TLC:
- Maximum Capacity: TLC SSDs can offer capacities ranging from 1TB to 4TB or even higher.
- Minimum Capacity: Available in smaller capacities starting from as low as 120GB.
MLC:
- Maximum Capacity: MLC SSDs commonly come in capacities ranging from 512GB to 2TB.
- Minimum Capacity: Available in smaller capacities starting from as low as 64GB.
SLC:
- Maximum Capacity: SLC SSDs typically offer capacities between 64GB and 1TB.
- Minimum Capacity: Available in smaller capacities starting from as low as 32GB.
Choosing the right capacity depends on your specific storage requirements. It is crucial to consider both your current needs and potential future growth.
When deciding between TLC, MLC, and SLC SSDs, it’s essential to consider the price per gigabyte, the value for money, and the available capacities.
Is SLC SSD the Most Durable Option Compared to TLC and MLC SSDs?
When considering the lifespan of SSDs, it’s important to compare SLC, TLC, and MLC options. One key factor in this comparison is the “ssd tlc vs mlc lifespan.” While SLC SSDs are generally regarded as the most durable option, offering a longer lifespan due to their high-level cell technology, TLC and MLC SSDs have advanced over time, narrowing the durability gap. Ultimately, your specific needs and budget will determine which SSD type is the most suitable choice.
Use Cases And Recommendations
Explore the differences between TLC, MLC, and SLC technology, and find recommendations for your specific use cases.
Use Cases For Tlc, Mlc, And Slc Ssds:
TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs are known for their cost-effectiveness and high storage capacity. They are ideal for consumer applications where cost per gigabyte is a significant factor.
Use cases include:
Consumer vs Enterprise Applications:
- TLC SSDs are suitable for everyday consumer applications, such as home computers and laptops, where cost-efficiency is essential, and performance requirements are moderate.
- Enterprise applications that involve large-scale data storage and processing may also benefit from TLC SSDs, especially for non-critical workloads and tasks.
Gaming and Multimedia:
- TLC SSDs can enhance gaming experiences by reducing loading times and providing faster data access. They are ideal for gamers who prioritize cost savings without sacrificing performance.
- For multimedia professionals who handle large media files frequently, such as video editing or 3D modeling, TLC SSDs offer sufficient storage capacity at a more affordable price point.
Data Center and Server Applications:
- While TLC SSDs are not typically recommended for mission-critical data center or server applications, they can be used for non-critical tasks, such as caching, content delivery networks (CDNs), or big data analysis where cost-efficiency is a priority.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs strike a balance between performance, endurance, and cost. They are suitable for applications that require higher reliability and endurance than TLC SSDs.
Use cases include:
Consumer vs Enterprise Applications:
- MLC SSDs are commonly found in high-performance consumer devices, such as high-end laptops or professional-grade cameras, where both performance and reliability are important factors.
- For enterprise applications that involve intensive workloads, such as database servers or virtualization environments, MLC SSDs can provide the required endurance and reliability.
Gaming and Multimedia:
- Gamers or content creators who demand higher performance and durability can benefit from MLC SSDs. These drives offer faster read and write speeds, reducing game loading times and improving multimedia editing efficiency.
Data Center and Server Applications:
- MLC SSDs are extensively used in enterprise-grade data centers and servers, especially in applications that require a balance of performance, endurance, and reliability.
- These include database servers, virtualization environments, and high-demand transactional systems.
SLC (Single-Level Cell) SSDs offer the highest level of endurance, reliability, and performance but at a higher cost. They are recommended for applications that demand guaranteed data integrity and require the utmost reliability.
Use cases include:
Consumer vs Enterprise Applications:
- SLC SSDs are rarely used in consumer applications due to their high cost. However, they may be suited for professionals who require uncompromising performance and durability, such as content creators or engineers working with critical data.
Gaming and Multimedia:
- SLC SSDs are not typically required for gaming or multimedia applications, as the performance difference compared to MLC or TLC SSDs might not be significant to justify the higher price tag.
Data Center and Server Applications:
- SLC SSDs are heavily utilized in mission-critical enterprise applications where data integrity and reliability are paramount, such as financial institutions, healthcare systems, or government agencies.
- They are ideal for workloads that involve constant read/write operations, ensuring data consistency and reliability.
Recommendations Based On Specific Requirements:
When choosing between TLC, MLC, and SLC SSDs, certain requirements must be considered.
Here are some recommendations based on specific priorities:
Speed and Performance Priority:
- For applications where speed and performance are key, MLC or SLC SSDs are recommended due to their faster read and write speeds compared to TLC SSDs.
Data Security and Reliability Priority:
- If data security and reliability are of utmost importance, SLC SSDs provide the highest level of endurance and reliability, ensuring data integrity.
Budget and Cost-effectiveness Priority:
- If you are on a tight budget, TLC SSDs offer an affordable solution without compromising storage capacity. They provide a balance between cost and performance for consumer applications.
Remember, when choosing the right type of SSD for your specific use case, it is essential to consider factors such as workload type, performance requirements, endurance, and overall budget.
Conclusion
SSD technology has come a long way, and the choice between TLC, MLC, and SLC can be overwhelming.
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to understand their differences before making a decision. While SLC offers the highest endurance and reliability, it comes at a higher cost.
MLC strikes a balance between endurance and affordability, making it a popular choice for many users. On the other hand, TLC is the most cost-effective option but has a lower durability compared to the other two.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider factors such as usage, workload, and data retention requirements.






