What is SSD: Everything You Need to Know!
The SSD is revolutionizing the data storage industry. While hard drives have been the standard for many years, SSDs can now store over 100 TB of data in a single drive. They’re far more durable and offer faster speeds than traditional hard drives.
As SSD has started to take off in the technology market, consumers are starting to ask more questions about it. We answer these questions and more, so that you have all the information you need to make an informed decision.
What does SSD stand for?
Solid State Drive, or SSD, is a type of storage media that uses solid state memory to store data. Because it has no moving parts, it is much faster and more reliable than traditional hard drives. This is in contrast to traditional hard drives, which use spinning disks to store data.
We will try to cover every question you have in your head related to SSD’s. We will be prioritizing questions that most people have on their mind.
What is SSD storage?
SSD storage is a non- volatile computer memory used for storing data in solid state drives. Unlike traditional disks, SSD storage does not rotate and uses flash memory chips rather than spinning disks to store data. This enhances performance and reduces power use and heat generation.
Non-volatile memory meaning SSD computer memory that retains data when not powered on. Unlike traditional disks, cached files are retained even if the power is removed.
When combined with a hard drive, this can create a hybrid drive to offer faster performance and more effective storage of multiple operating systems or apps at once.
SSDs are more reliable than HDDs because data loss can be kept to a minimum due to extreme shock resistance, wear levels and largely reduces random corruption issues.
As NAND is used in them, reducing the bits overwritten etc. greatly reduces operation time of these devices, thereby boosting their efficiency substantially. Size wise, they ‘re close to those of HDD but much smaller both electrically and physically.
NAND Stand for Non – Dynamic “, a type of computer processor that stores data using cells made out of resistive materials such as poly silicon, based on the phenomenon known as tunneling. Unlike traditional storage media (magnetic disks), they do not require recording spindles or physical moving parts over heads to store information!
Their operation frequency is much faster also too, compared to HDD, as flash components are designed for high-speed operations which further translates into their read/write speeds and thus power consumption that is significantly less than HDDs of the same size and hence converts less power from the source.
What is SSD in a laptop?
In a laptop, solid-state drive (“SSD” or “solid state”) is the primary storage device. SSDs have better power consumption characteristics than traditional hard disk drives, so they need less energy to run with their idle functions turned off during sleeping and suspension.
To understand why this is needed, let’s first understand what exactly we are using in laptops that can be compared here?

Old Laptops use cheap components like motherboards, batteries etc. which cannot perform at all when overloaded, but high speed memory chips called DRAM can give a huge performance boost if properly integrated into these circuits.
More importantly, during frequent use of notebook operations that yield a lot of heat from the system components, If this fails to dissipate properly and will cause huge lead through leakage, causing unstable operation.
What does SSD do?

An SSD (solid-state drive) is the latest form of memory technology which replaces hard drives in computers. While both are types of storage devices, an SSD has no moving parts and draws much less power for data processing.
As a result, it has very fast speed and can store large amounts of information per unit cost as well as decreasing irrelevant environmental pollution.
Solid-state drives have become more and more popular over the years due to their higher read/write speeds and improved reliability over hard drives with similar capacities.
Pros: Faster reading/writing cycles, better speed, no mechanical parts to fail
Cons: Very expensive
What is the difference between SSD and HDD?
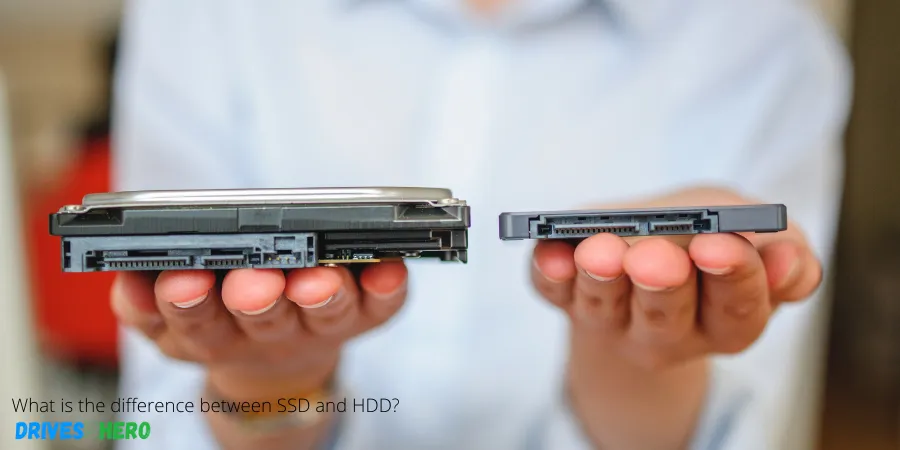

Before you can start picking the perfect SSD and HDD, here are a few differences that may help to enlighten your choice-making process:
An SSD is designed for performance that’s why it uses a controller to take demanding tasks off the processor and do everything automatically.
While an HDD is designed for capacity and price, which is why it has no built-in controller or support from Windows but still can handle most workloads with ease.
On top of that, an SSD will be more expensive than an HDD and will have a shorter lifespan, but an SSD has much faster performance and you’ll rarely see data corruption.
SSD vs. HDD Pricing
Though SSD have been around for a while, they are not yet widely adopted in the PC industry due to their significantly higher price than traditional hard drives.
Prices of SSDs often range from $100 to $550, compared to HDDs at about $50 per terabyte (TB). SSD pricing is getting closer to HDD prices all the time and fall just short, with a few good deals still out there.

While current SSD costs are steeply higher than comparable hard drives, the gap will decrease through 2016 and 2017. Right now, you can get an mSATA SSD with two or four times the capacity for about twice as much money.
For the last few years, SSDs have been steadily decreasing in price to the point where they can be as cheap as HDDs!
This is one important difference between them; because SSDs are more expensive than HDDs, newer machines with an SSD usually come with a large premium that wouldn’t be necessary if a comparable machine used an HDD instead.
Example: Samsung 850 EVO 250GB drive costs $115 compared to around $62 for an equivalent size WD 2TB hard drive.
How Much Faster is SSD than HDD?

There are different form factors of both the HDD and the SSD. For SSD NVme , SATA, M.2, PCIe, on the other hand HDD start from 5400RPM to 10,000 or higher RPM.
If you select Samsung 980 PRO w/ Heatsink PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSD , 1TB or 2 TB storage you will get upto 7000 MB/s reading speed and for writing speed you can get upto 5000 MB/s
On The other hand The latest HDD 7200rpm will deliver you up to 550 MB/s. You can never compare HDD outdated speed with the latest SSDs, they are too different.
SSD vs. HDD Reliability and Durability
The life of an SSD depends on how many cycles it gets, and how long it is used before being replaced.
As a rule of thumb, it takes a SSD about 5-10 years to reach a point where it can no longer reliably store data. That said, it is possible for an SSD to fail in some circumstances, which we’ll cover in another post.
A typical HDD can fail after a few years and usually needs to be replaced. While a SSD has a much longer lifespan, and in many cases, it will outlive the device it’s installed on.
HDDs have a lot more moving parts and are thus much more susceptible to mechanical failure. While SSDs have no moving parts, they also store data in flash memory. Which can be erased and written to multiple times before it eventually fail.
Which is better ssd or hdd?
This is a question that doesn’t have a clear cut answer. It depends on your needs and what you’re using your computer for.
If you need a lot of storage space, then an HDD is the best option. If you need a computer that is fast and responsive, then an SSD is the better choice.

HDDs are larger, slower, and cheaper than SSDs. They are good for storing large files such as videos or photos. SSDs are smaller, faster, and more expensive than HDDs. They are good for storing programs and applications that need to be accessed quickly.
If you’re not sure which option is best for you, consult with a computer technician. They can help you decide which option is best for your computer needs.
What Are the Benefits of Using An SSD?
There are several benefits to using an SSD, including:
Faster access times: Since SSDs use solid state memory, they can access data much faster than traditional hard drives. This makes them ideal for tasks that require quick response times, such as gaming or web browsing.
Less power consumption: SSDs consume less power than traditional hard drives, which can result in longer battery life for laptops and other portable devices.
Cooler operating temperatures: Traditional hard drives generate a lot of heat due to their spinning disks. SSDs, on the other hand, generate very little heat, making them a good choice for laptops and other systems that need to run quietly.
Lightweight: SSDs are lighter than traditional hard drives, which is ideal for mobile devices and small form factor computers.
Thanks to SSD technology, now we can get larger spaces for laptops,desktops, tablets, flash drive, even smartphone device form factors. Most ssd drives come with a 3-5 year warranty in comparison to the 1-3 years for normal HDD. With this advantage comes disadvantages such as their price which tend to be higher compared to their storage capacity.
SSD Specification Overview
The SSD uses the NAND Flash to store data. Each sector is small, so the size gets larger as the storage capacity increases.
Here is the quick overview on ssd’s from factor, interface, capacity and few manufacturer:
SSD From Factor: Quick Overview
There are multiple types of SSDs on the market, with each type having its own set of benefits and drawbacks. The most common types of SSDs are given bellow in drives hero future content we will discuss each type in detail.
- M.2 SSD
- 2.5 inch / 2.5-inch Serial ATA (SATA)
- mSATA
- NVme
- SSD Add-in Card (AIC)
- PCIe NVMe M.2
SSD Interface: Quick Overview
- PCIe Gen 4 * 4 NVMe 1.3c
- PCIe Gen 3.0 * 4 NVMe 1.4c
- PCIe Gen 3.0 * 4 NVMe 1.2c
- PCIe Gen 3.0 * 4 NVMe 1.1
- SATA 6 Gb/s Interface
- SATA 1.5 Gb/s Interface
SSD Capacity: Quick Overview
- 2TB & Up
- 1TB to 1.9TB
- 480GB to 999GB
- 240GB to 479GB
- 120GB to 239GB
- Under 120GB
SSD Manufacturer
- SAMSUNG
- WESTERN DIGITAL
- SEAGATE
- Toshiba
- CRUCIAL
- KINGSTON
- LEXAR
- CORSAIR
- ADDLINK
- INTEL SSD
- ADATA XPG
- SABRENT ROCKET
- SANDISK
Conclusions
While you’re reading this, your laptop is probably running on a hard drive. You might not even know it, because most laptops use hybrid drives that combine an SSD with a traditional hard drive.
We try to provide all the basic information to anyone who wants to know about SSD, SSD manufacturers, SSD types and sizes. We’ll get into the nitty-gritty of things such as interface speeds, capacity and other important aspects in the future articles
Drives Hero is a dedicated site for SSD, HDD and other drives. If you have any questions, feel free to comment, we will contribute to this article as soon as possible.
FAQ’s On SSD
What does SSD mean?
Solid State Drive. A type of data storage that uses interconnected flash-memory chips rather than spinning magnetic disks. SSD is more faster
and reliable than HDD.
What is SSD drive?
A drive that uses Solid State Drive, which is made up of interconnected flash-memory chips. You may have heard of a web hosting company that gives SSD Drive.
Is SSD better than HDD?
It depends on your needs. SSDs are faster and more expensive than HDDs, while HDDs are larger, slower, and cheaper than SSDs.
What is an SSD card?
An SSD card is a type of data storage that uses interconnected flash-memory chips. It is a smaller and faster alternative to an HDD.
What does M.2 mean?
It is an interface for PCIe-based NVMe drives with the form factor of a small rectangular module similar to an expansion card that uses PCI Express Gen 3 x4 lanes and supports SATA, PCIE or NVMe standards.