How to Read Nvme Ssd
If you’re looking to upgrade your computer’s storage, you might be wondering whether to get an NVMe SSD. These drives are the latest and greatest in terms of solid state storage, offering faster speeds and lower latency than their SATA counterparts. But what do you need to know before making the switch?
Here’s a quick guide on how to read NVMe SSDs.
When shopping for an NVMe SSD, the first thing you’ll want to look at is the drive’s capacity. Currently, most NVMe drives come in either 250GB or 500GB sizes, with 1TB models starting to become more common.
If you have a lot of data to store, you’ll want one of the larger capacities; otherwise, a smaller drive will suffice.
Once you’ve decided on a capacity, take a look at the drive’s speed. The vast majority of NVMe drives are rated for speeds of 3200MB/s or higher, which is significantly faster than even the fastest SATA SSDs.
If speed is important to you (for example, if you’re using your computer for gaming), make sure to get anNVMe drive that can hit those high speeds.
- Download and install the appropriate NVMe driver for your operating system
- Connect the NVMe SSD to your computer
- Make sure it is properly connected and seated in the drive bay
- Power on your computer and wait for it to boot into your operating system
- Locate the new drive in your operating system’s file manager (e
- , Windows Explorer, Finder)
- It should show up as a new drive with unallocated space
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select “Format
- ” Choose whichever file format you want (NTFS, exFAT, etc
- ) and give the drive a name if prompted
- Click “OK” to begin formatting the drive
- 6 once formatting is complete, the drive will be ready to use like any other storage device
How Do I Retrieve Data from Nvme Ssd?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a newer protocol for accessing high-speed storage media, specifically SSDs. This article will explain how to retrieve data from an NVMe SSD.
To start, you need to connect the NVMe SSD to your computer.
This can be done via a USB port or through a PCI Express slot. Once the connection is made, you will need to format the drive before you can use it. The process for formatting an NVMe SSD is similar to formatting any other type of drive; however, there are some specific steps that must be followed when using this type of drive.
Once the drive is formatted, you can begin copying data to and from the drive. When transferring data to an NVMe SSD, it is important to use a tool that supports the TRIM command. TRIM helps keep the drive perform at its best by ensuring that only valid data blocks are written to the drive.
Without TRIM support, write performance on an NVMe SSD will eventually degrade as invalid data blocks accumulate on the drive.
How Do I View Nvme?
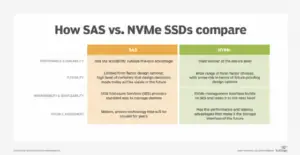
NVMe is a high performance, scalable, non-volatile memory express bus. It was designed to address the needs of enterprise and client applications that require low latency, high input/output operations per second (IOPS), and high bandwidth. NVMe has been gaining popularity in the SSD market as it offers lower power consumption and faster data transfers than traditional SAS or SATA SSDs.
To view an NVMe drive, you’ll need to connect it to your computer using an M.2 connector on the motherboard or a PCIe adapter card. Once connected, you can use any disk management tool to format and partition the drive. Windows 10 includes support for NVMe drives out of the box, so you shouldn’t have any trouble getting started with one.
How Do I Read an M 2 Ssd?
M2 SSDs are the next generation of solid state drives, offering faster data transfer speeds and lower power consumption than their predecessors. Here’s how to read one:
1. Make sure your computer supports M2 SSDs.
Most newer computers should, but you’ll want to check your motherboard’s specifications just to be sure.
2. Connect the SSD to your computer using an M2 to SATA adapter or cable. You’ll need to connect it to a SATA port on your motherboard – most motherboards have at least two.
3. Install any necessary drivers for the SSD. This may be done automatically by your operating system, or you may need to download and install them manually from the manufacturer’s website.
4. Format the SSD as you would any other drive.
This can be done in Windows’ Disk Management tool or in macOS’ Disk Utility application, among other places. Be sure to choose the “Quick Format” option to ensure that no data is left behind on the drive.
5a) For Windows users: Once formatted, open up File Explorer and find your new drive under “This PC.”
Right-click on it and select “Format.” In the window that pops up, make sure that NTFS is selected as the file system and click “Start.” The format process will take a few minutes depending on the size of your drive; when it’s finished, click “Close.”
5b) For macOS users: Launch Disk Utility (it’s located in Applications > Utilities).
What is the Read And Write Speed of Nvme Ssd?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high performance, low latency storage interface designed for next generation flash-based solid state drives (SSDs). NVMe is the successor to the AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) storage protocol and utilizes a much more efficient command set that reduces CPU overhead and enables lower latency.
NVMe SSDs offer extremely fast read and write speeds, making them ideal for demanding applications such as video editing, 3D rendering, gaming, and data analytics.
The typical read speed of an NVMe SSD is around 2200 MB/s, while the write speed is typically around 1500 MB/s. However, there are some newer models that offer even higher speeds of up to 3500 MB/s.
Nvme Ssd 1Tb
If you’re looking for an upgrade to your computer’s storage, you may be wondering whether to get an NVMe SSD or a regular SSD. Both have their advantages, but ultimately it depends on your needs. In this blog post, we’ll go over the differences between NVMe and regular SSDs so you can make the best decision for your computer.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a newer type of SSD that offers faster speeds and lower latency than regular SSDs. NVMe drives are available in both M.2 and PCI Express form factors and use the PCIe bus for communication with the motherboard. This allows them to offer much higher sequential read/write speeds than regular SATA-based SSDs.
Regular SSDs are available in both 2.5″ and M.2 form factors, but they use the slower SATA bus for communication with the motherboard. This means that they tend to have lower sequential read/write speeds than NVMe drives. However, they’re often cheaper and more widely available than NVMe drives.
So which one should you choose? If speed is your top priority, then go with an NVMe drive. If price is your main concern, then a regular SSD will suffice.
Recover Data from Nvme Ssd
If you have an Nvme SSD, you may be wondering how to recover data from it. This can be a tricky process, but there are a few things that you can do in order to try and get your data back.
First, if the drive is not physically damaged, you can try using a data recovery software program.
These programs can often times recover data from drives that have been formatted or corrupted.
Another option is to send the drive to a professional data recovery company. These companies specialize in recovering data from all types of storage devices, including SSDs.
They will usually be able to recovered your data for a fee.
Finally, if all else fails, you can try opening up the drive and manually extracting the data yourself. This is definitely not for the faint of heart, and should only be attempted if you are confident in your abilities.
If you do decide to go this route, make sure that you have all of the proper tools and knowledge before beginning.
How to Recover Data from Ssd Dead Laptop
One of the most frustrating things that can happen to a computer user is losing data. This is especially true if the data is important, such as work documents or family photos. If you have a dead laptop with an SSD (solid state drive), there is still hope that you can recover your data.
Here are some tips on how to go about recovering data from a dead SSD laptop:
2. Once the SSD is removed, you will need to connect it to another computer using a USB cable or SATA adapter. 3. Once the SSD is connected, you can then use specialized software to scan for and recover any lost data. There are many different types of recovery software available, so be sure to research which one would be best for your needs before purchasing anything.
4. After you have recovered your data, be sure to backup everything onto another storage device so that you don’t lose it again in the future!
Nvme Vs Ssd
There are many different types of storage devices on the market today, and it can be hard to decide which one is right for you. If you’re looking for speed and performance, then you’ll want to choose an NVMe SSD. Here’s a look at the differences between NVMe and SSDs so you can make the best decision for your needs.
NVMe drives are the newest type of SSD on the market. They offer several benefits over traditional SSDs, including faster speeds, lower latency, and improved power efficiency. NVMe drives are available in both M.2 and PCI Express form factors, making them compatible with a wide range of computers.
One of the biggest advantages of NVMe drives is their speed. They typically offer read speeds of up to 3200 MB/s and write speeds of up to 1900 MB/s. That’s much faster than most SATA-based SSDs, which top out at around 550 MB/s.
This extra speed is thanks to the way NVMe drives connect to your computer’s motherboard.
While SATA-based SSDs use the older AHCI interface, NVMe drives use a newer interface called NVM Express (NVME). The NVME interface allows for much higher data transfer rates than AHCI, which means that NVMe drives can take full advantage of their high speed potential.
Another advantage of NVMe drives is their low latency. Latency is the time it takes for your computer to start reading or writing data after you’ve issued a command. With traditional SATA-based SSDs, there can be quite a bit of latency due to the need to first convert commands from your CPU into a format that can be understood by the drive controller chip.
But since NVMe uses a direct CPU-to-drive connection, there’s no need for this conversion step, resulting in lower latency and better overall performance.
Conclusion
This blog post covers the basics of how to read an NVMe SSD. It explains what NVMe is and why it’s important, as well as how to physically connect an NVMe drive to your computer. The post also covers some troubleshooting tips in case you have trouble getting your drive to show up.