Ssd Slc Vs Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc: Which Is Preferable?
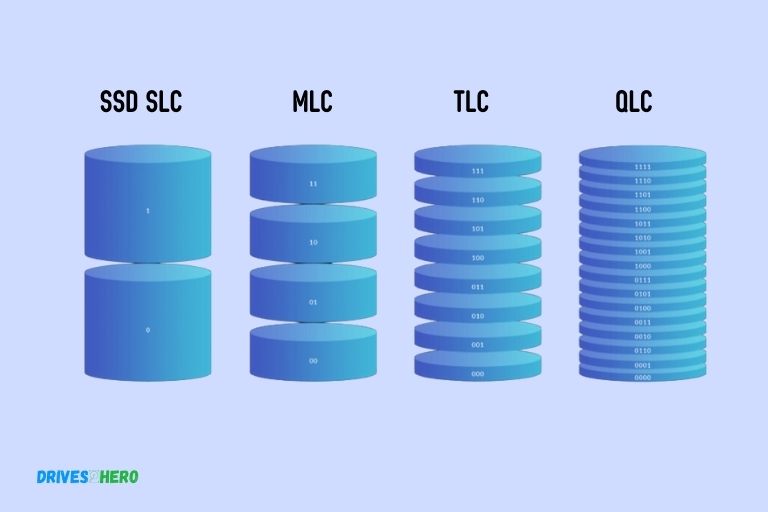
SSD SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC represent the different types of NAND flash memory used in solid-state drives (SSDs).
SLC (Single-Level Cell) stores one bit of data per cell, offering the highest endurance and performance, but also the highest cost.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) stores two bits per cell and strikes a balance between cost and performance. TLC (Triple-Level Cell) stores three bits per cell, providing a lower cost but with reduced performance and lifespan.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) stores four bits per cell, offering the highest storage density and lowest cost but with the lowest endurance and performance.
SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC stand for Single-Level Cell, Multi-Level Cell, Triple-Level Cell, and Quad-Level Cell, respectively. Each refers to the type of NAND flash memory used in SSDs.
When it comes to choosing the right type of solid-state drive (SSD) for your specific needs, understanding the differences between SSDs with different memory cell types is crucial.
Key Takeaway
Performance Comparison
SSD performance can vary depending on the type of memory cells used: SLC, MLC, TLC, or QLC. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision for your storage needs.
Speed And Latency: Slc Vs Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc
When it comes to speed and latency, the type of NAND flash memory used in SSDs plays a crucial role.
Let’s take a closer look at the performance comparison between SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC SSDs:
Single-Level Cell (SLC):
- Provides the fastest read and write speeds among the four types.
- Offers low latency, making it ideal for applications that require high-speed data access.
- SLC SSDs excel in tasks that involve heavy workloads and real-time processing.
Multi-Level Cell (MLC):
- Compared to SLC, MLC SSDs have slightly slower speeds.
- While they may not match SLC in terms of performance, MLC SSDs are still quite fast and suitable for most consumer and enterprise applications.
- MLC offers a good balance between speed and cost, making it a popular choice for many users.
Triple-Level Cell (TLC):
- TLC SSDs are further down the speed ladder but are more affordable than both SLC and MLC options.
- While not as fast as SLC or MLC, TLC SSDs deliver respectable performance for everyday use.
- TLC SSDs are commonly found in consumer devices such as laptops and desktop computers.
Quad-Level Cell (QLC):
- QLC SSDs are the slowest among the four types in terms of read and write speeds.
- However, they offer the highest storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte.
- QLC SSDs are often used in applications where large storage capacity is more important than raw speed, such as mass storage in data centers.
Endurance And Lifetime: Slc Vs Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc
The endurance and lifetime of an SSD are determined by factors such as how many times the memory cells can be reliably programmed and erased.
Here’s a comparison of SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC in terms of their endurance and lifetime:
Single-Level Cell (SLC):
- SLC SSDs have the highest endurance, capable of withstanding a significant number of program/erase cycles.
- They typically have a longer lifespan compared to other types of SSDs.
- SLC SSDs are commonly used in enterprise environments where durability is crucial.
Multi-Level Cell (MLC):
- MLC SSDs have a lower endurance than SLC, but they still offer good durability.
- With proper management, MLC SSDs can last for many years, making them suitable for consumer and some enterprise applications.
Triple-Level Cell (TLC):
- TLC SSDs have lower endurance than both SLC and MLC options.
- While they may not last as long as SLC or MLC, TLC SSDs still have a reasonable lifespan for everyday use.
Quad-Level Cell (QLC):
- QLC SSDs typically have the lowest endurance among the four types.
- However, advancements in technology and controller algorithms have improved the lifespan of QLC SSDs over time.
- QLC SSDs are best suited for applications that prioritize capacity over longevity.
Write Amplification: Slc Vs Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc
Write amplification refers to the multiplying effect of write operations on NAND flash memory.
Here’s a comparison of SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC SSDs in terms of write amplification:
Single-Level Cell (SLC):
- SLC SSDs generally have the lowest write amplification due to their simpler architecture.
- This means that SLC SSDs require fewer program/erase cycles, resulting in reduced wear and tear on the memory cells.
Multi-Level Cell (MLC):
- MLC SSDs have a higher write amplification compared to SLC SSDs.
- While still manageable, the increased write amplification may impact the longevity of the drive to some extent.
Triple-Level Cell (TLC):
- TLC SSDs tend to have higher write amplification than both SLC and MLC SSDs.
- However, advancements in software algorithms and controller technologies have helped mitigate this issue.
Quad-Level Cell (QLC):
- QLC SSDs exhibit the highest write amplification among the four types.
- Controlling write amplification is crucial to ensuring the longevity and performance of QLC SSDs.
Cost And Capacity: Slc Vs Mlc Vs Tlc Vs Qlc
The cost and capacity of SSDs are closely related to the type of NAND flash memory used.
Let’s compare SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC in terms of cost and capacity:
Single-Level Cell (SLC):
- SLC SSDs are the most expensive option due to their superior performance, endurance, and write amplification characteristics.
- They typically offer lower storage capacity compared to the other types.
- SLC SSDs are commonly used in enterprise applications that demand top-tier performance and durability.
Multi-Level Cell (MLC):
- MLC SSDs strike a balance between cost, performance, and capacity.
- They are more affordable than SLC SSDs and offer higher storage capacity.
- MLC SSDs are widely used in both consumer and enterprise applications.
Triple-Level Cell (TLC):
- TLC SSDs are relatively inexpensive compared to SLC and MLC options.
- They provide higher storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte.
- TLC SSDs are the most common type found in consumer devices.
Quad-Level Cell (QLC):
- QLC SSDs are the most cost-effective option among the four types.
- They offer the highest storage capacity but at a slightly lower performance level.
- QLC SSDs are suitable for applications that require large storage capacity without breaking the bank.
Consumer Vs Enterprise Ssd Performance
When comparing consumer and enterprise SSDs, there are some notable performance differences to consider:
Consumer SSDs:
- Designed for everyday use and consumer applications.
- Typically prioritize cost and capacity over ultimate performance.
- Offer a good balance between affordability and solid performance for most users.
Enterprise SSDs:
- Engineered for demanding environments and heavy workloads.
- Focus on maximizing performance, endurance, and reliability.
- Often incorporate advanced features and technologies to cater to enterprise-level requirements.
The performance, endurance, write amplification, and cost considerations differ across SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC SSDs. Each type has its advantages and is suitable for specific use cases, whether for consumer or enterprise applications.
Choosing The Right Ssd
Choosing the right SSD involves understanding the differences between SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC technology, which impact performance and durability.
Factors To Consider: Workload, Budget, And Use Case
When choosing the right SSD, several factors should be taken into consideration, including workload, budget, and use case. By evaluating these factors, you can ensure that you make the best decision for your specific needs.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Workload: Assess the demands of your workload, including the type of tasks you frequently perform and the level of data transfer required. This will help you determine the necessary storage capacity and performance specifications.
- Budget: Set a realistic budget for your SSD purchase. SSDs come in a range of prices based on factors such as capacity, speed, and technology. It’s important to strike a balance between performance and cost.
- Use Case: Consider how you plan to use your SSD. Different use cases require varying levels of speed, endurance, and reliability. Whether you are a gamer, content creator, or business professional, identifying your specific use case will guide you in choosing the right SSD.
Performance Demands: Gaming, Content Creation, And Business Use
Depending on your specific needs, different performance demands may be crucial.
Here’s a breakdown of what to consider for different use cases:
- Gaming: If you’re a gamer, you’ll want an SSD that delivers fast loading times, smooth gameplay, and minimal latency. Look for SSDs with high random read and write speeds to ensure optimal gaming performance.
- Content Creation: Content creators often require SSDs with high write speeds to handle large file transfers and editing tasks. Look for SSDs with strong sequential and random write performance to support your content creation workflow.
- Business Use: For business professionals, SSDs that prioritize reliability and data integrity are crucial. Consider SSDs with features like power loss protection and strong endurance ratings to ensure smooth operation and data security.
Balancing Speed, Endurance, And Cost: Ssd Technology Comparison
SSDs are available in different technologies, each offering unique benefits and trade-offs.
Take into account the following technology types when making your decision:
- SLC (Single-Level Cell): SLC SSDs excel in terms of speed, endurance, and reliability. However, they tend to be expensive and have lower storage capacities. Ideal for professional use cases that require top-tier performance.
- MLC (Multi-Level Cell): MLC SSDs strike a balance between performance, cost, and endurance. They offer higher storage capacities compared to SLC, making them suitable for a range of use cases, including gaming and content creation.
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell): TLC SSDs prioritize cost-effectiveness and high storage capacities. While they may not match the endurance of SLC or MLC SSDs, they still provide sufficient performance for everyday use and are well-suited for budget-conscious consumers.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell): QLC SSDs offer the highest storage capacities at a lower cost. However, they sacrifice endurance and performance compared to other SSD technologies. QLC SSDs are ideal for users with large data storage needs but less demanding workloads.
Ssd Recommendations Based On User Needs
Based on the factors described above, here are some SSD recommendations tailored to different user needs:
- Gamers: Opt for MLC or TLC SSDs with high random read and write speeds to support fast loading times and smooth gameplay. Aim for capacities that accommodate your game library.
- Content Creators: Choose MLC or TLC SSDs with strong sequential and random write speeds to handle large files and demanding editing tasks. Consider higher capacity options to store your media files.
- Business Professionals: Prioritize reliability and data security with MLC or SLC SSDs featuring features like power loss protection and high endurance ratings. Opt for capacities that meet your business needs.
What are the differences between SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC SSDs, and which one is the best choice?
When it comes to SSDs, understanding the differences between SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC is crucial. SSD TLC vs MLC: The Superior Choice will help shed some light on the matter. SLC (Single-Level Cell) provides the highest performance, reliability, and endurance but comes at a higher cost. MLC (Multi-Level Cell) balances performance and cost-effectiveness, while TLC (Triple-Level Cell) offers higher storage capacity at a more affordable price but sacrifices some performance and endurance. QLC (Quad-Level Cell) offers even higher capacity but further sacrifices performance and endurance. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
Future Trends And Emerging Ssd Technologies
As technology evolves, SSDs continue to advance.
Here are some notable trends and emerging SSD technologies to keep an eye on:
- PCIe 4.0: With faster data transfer speeds, PCIe 4.0 SSDs offer improved performance for demanding tasks. As the adoption of PCIe 4.0 becomes more widespread, it will become a popular choice in various use cases.
- NVMe: Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) SSDs provide even faster data transfer rates and lower latency compared to traditional SATA SSDs. NVMe SSDs are gaining popularity and are recommended for users seeking top-tier performance.
- 3D NAND: This technology allows for higher storage capacity by stacking memory cells vertically. As 3D NAND becomes more prevalent, SSDs will offer larger capacities without compromising performance.
- Optane: Intel Optane SSDs utilize 3D XPoint memory technology, providing a blend of high performance and endurance. Optane SSDs are particularly suitable for high-intensity workloads in professional settings.
By staying informed about these emerging trends and technologies, you can make more informed decisions when choosing an SSD that meets your future requirements.
Conclusion
As you now know, there are various types of SSDs available in the market – SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC. Each type offers different performance levels, endurance, and price points.
SLC SSDs, with their single-cell technology, provide exceptional speed and durability, making them ideal for high-intensity workloads and enterprise applications.
MLC SSDs, with their multi-level cell design, strike a balance between performance and cost, making them suitable for a range of applications. TLC SSDs, with their triple-level cell structure, offer lower cost per gigabyte and are well-suited for consumer-grade devices.
Finally, QLC SSDs, with their quad-level cell technology, provide high-capacity storage at an affordable price, although with reduced endurance. It is essential to understand the specific requirements of your workload and budget when choosing between these SSD types.






